Raynaud's Disease (Phenomenon)
Raynaud's Disease Plot Summary:
It is a disease that is usually seen in young girls and rarely in boys and is accompanied by spasm (shrinkage and narrowing) of the small diameter arteries of the hand, which may improve with age. In emotional situations such as cold, stress, excitement, the hands become pale, blue, and cold, and in the future, excessive bruising, wound opening, and infection may occur on the fingertips. The reason is that stress causes excessive sympathetic activity and causes vasospasm (constriction) in the distal, small-diameter arteries of the hand. Delay in diagnosis causes this advanced condition. Diagnosis is usually made during examination; additionally, angiography or computed tomographic angiography may be helpful. The color change on the hands is evident with the hot and cold water test.
After Raynaud's Disease Diagnosis
Tanı konulduktan sonra tedavinin başında stresin azaltılması gelir ve hastanın takibi yapılır, şikayetlerin artması veya düzelmemesi durumunda, %98 oranında iyileşme sağlayabilen sempatektomi ameliyatı yapılması en uygun tedavidir. Boyun ve göğüs bölgesine yapıldığı için servikal veya torakal sempatektomi ameliyatı olarak adlandırılır.
This surgery can be caused by cold, stress, etc. It is performed to eliminate the effect of sympathetic activity in that area, which is effective in certain situations and causes vasospasm (constriction) of the arteries.
By entering through a small incision in the armpit, the inner-back side of the chest is reached and the sympathetic chain is removed. There are no complications in experienced hands. However, the sympathetic chain must be completely removed, so the endoscopic and clip (staple) techniques used for sweating are not successful.
Within the first day and 1 month after the surgery, healing accelerates, hands become warmer, and normal color prevails.
All About Raynaud's Disease
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul
Raynaud's disease is a vascular disease that usually affects the fingers and toes, occurs as a result of reduced blood flow due to narrowing of the vessels, and can cause pain in the future. In some cases, it can also be seen in the ear or nose. It is a disease more common in young women. Situations in which Raynaud's disease occurs on its own are called primary Raynaud's, while cases accompanied by rheumatic diseases or other diseases are called secondary Raynaud's disease. Therefore, the most appropriate treatment method should be decided after the necessary analysis, tests and evaluations in the treatment of the disease.
Raynaud's Disease Surgery
It may be decided to treat Raynaud's disease with surgery if it is deemed necessary. Treatment with surgery; It is based on the elimination of the sympathetic chain, that is, the sympathetic nervous system activity that causes the finger veins to constrict, by entering through a small area on the inner side of the chest, called thoracic sympathectomy.
Symptoms of Reynaud's disease should not be neglected and it should be checked by a specialist physician to determine whether the disease is caused by a disease in the first place. Reynaud's disease, which is called primary and occurs on its own, can cause different diseases in the future if left untreated. Therefore, it is extremely important to determine appropriate treatment options by performing the necessary clinical examination, tests and analyzes in the treatment of this disease.
Operation Time
2-3 Hours
Recovery Time
4-6 Weeks
Discharge Time
1-2 Days
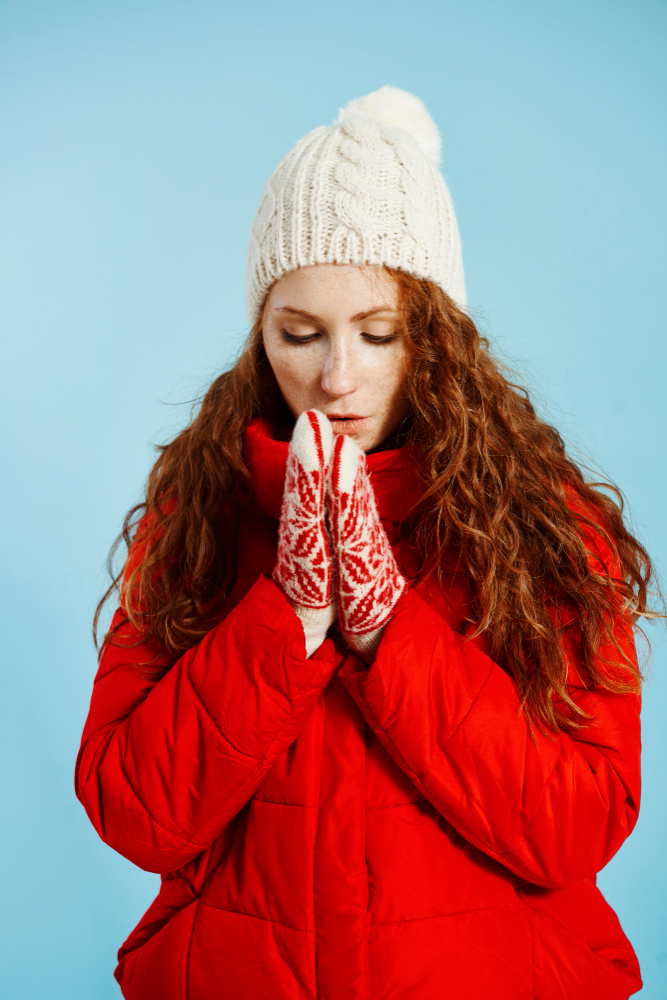

What Causes Raynaud's Disease?
The definitive diagnosis of Reynaud's disease is made by blood tests, finger blood pressure and blood flow measurements, as well as clinical examination.
Although the cause of Reynaud's disease is not fully known, it is considered that cold, stress, some drug use, the person's psychological state and cigarette consumption trigger the disease. As with the secondary Raynaud phenomenon, Reynaud's disease may occur due to some diseases such as rheumatological disease. Therefore, when Raynaud's symptoms are observed, it should be investigated whether there is an underlying disease.
Complaints of Raynaud's Patients
- Color change in the form of paleness in the hands and fingers
- Bruising of hands in cold weather
- Cold hands, feeling cold
- Increased bruising on the hands during changes between hot and cold
- Occurrence of painful crises in the future

Over 20 Years of Experience
Having More than 20 Years of Experience in the Field of Cardiovascular Surgery Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul, He Has Improved The Health And Cured Many Patients.
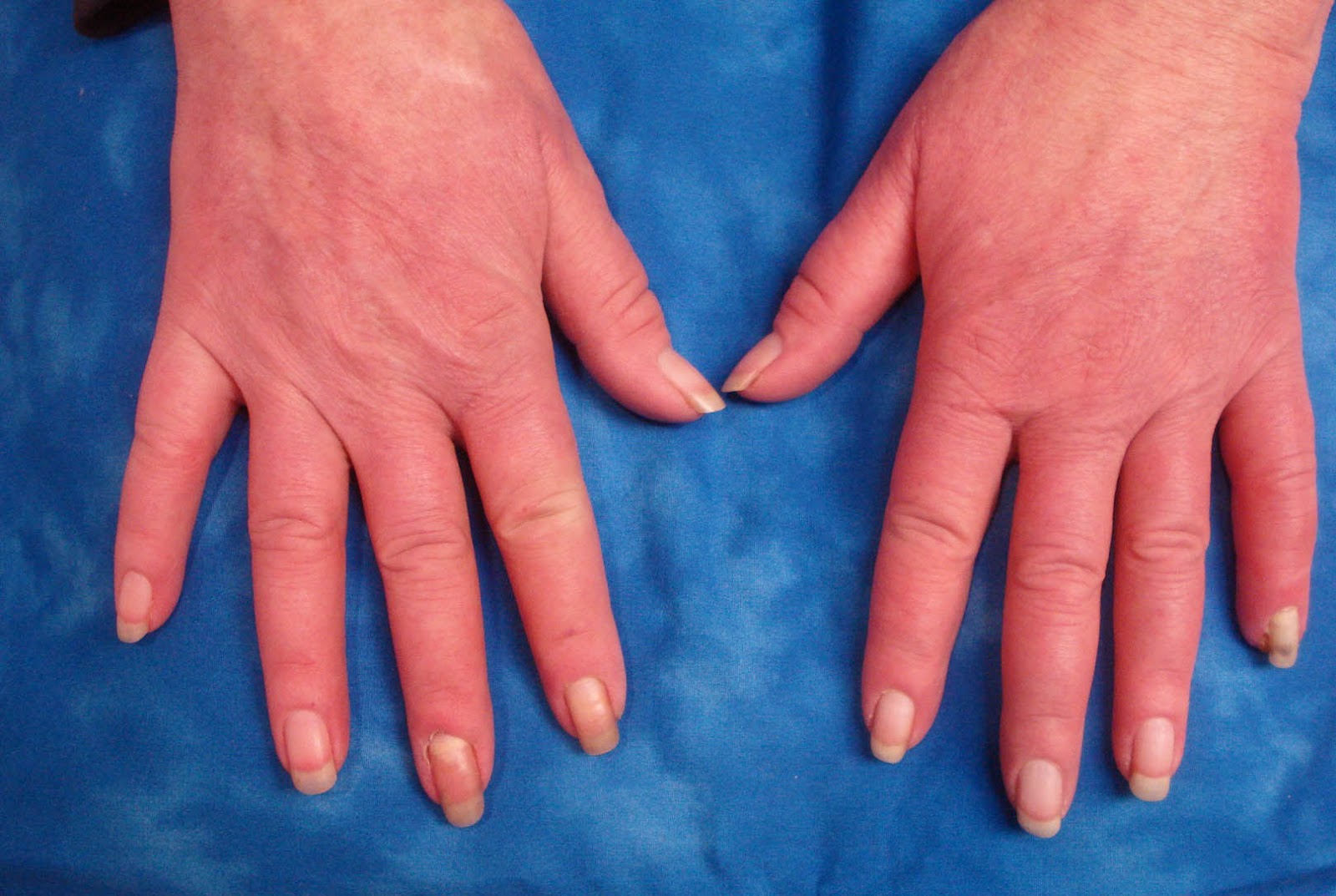
Raynaud's Disease Symptoms
- Color change in the form of paleness in the hands and fingers
- Bruising of hands in cold weather
- Cold hands, feeling cold
- Increased bruising on the hands during changes between hot and cold
- Occurrence of painful crises in the future
Raynaud's Disease Symptoms Brief Information About
Raynaud's Disease Treatment
In the treatment of Raynaud's disease, the answer to the question of whether the disease is primary or secondary Raynaud's phenomenon must first be investigated. In Reynaud's phenomenon accompanied by other diseases such as rheumatic disease, the most appropriate treatment options should be determined after the necessary evaluations are made along with this disease.
In the treatment of Raynaud's disease, protection can be provided by taking protective measures against cold such as using hot water and using gloves in cold weather. The use of medication is one of the methods used in the treatment of Reynaud's disease. While Raynaud's disease can sometimes be cured with a very simple drug treatment, treatment for this disease that continues in the long term; It is based on the elimination of the sympathetic chain, that is, the sympathetic nervous system activity that causes the finger veins to constrict, by entering through a small area on the inner side of the chest, called thoracic sympathectomy. In this treatment, the patient becomes very comfortable and his past complaints disappear, and his hands even begin to overheat.
Location
Merkez, Hastanesi Sokak No:2, 34245 Gaziosmanpaşa/İstanbul
Contact
dryavuzbesogul.com
Our watches
Contact Us


Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul: Academic Statement on Raynaud's Disease
It is characterized by cyanosis, pallor, pain and numbness, often seen in the hands, which can be attributed to connective tissue disease or increased sympathetic activity, although the cause is not fully known, often in young ages. It occurs as a result of spasm of small diameter arteries. Sometimes excessive sweating may be observed in the hands, but the sweating is cold and the hands become cold. Symptoms are triggered by cold, stress and excitement. In extremely advanced cases, necrosis and even gangrene may occur at the fingertips. Finger amputation may be required as a result of treatment not performed on time. Diagnosis is easily made clinically. Hot and cold water tests also help in diagnosis. The angiographic image is characterized by the lack of blood flow to the distal arteries and the absence of collaterals.
Treatment
Tedavide stres ve soğuktan uzak durması ellerini sıcak tutması önem taşır. Şikayetlerinin artması ve nekroz görülmesi durumunda gecikmeden torakal sempatektomi yapılması uygundur. Göğüs yan koltukaltından 2. İnterkostal aralıktan toraksa girilerek sempatik ganglion ve zincir çıkarılır. Ameliyatın herhangi bir komplikasyonu yoktur. Operasyondan hemen sonra ellerde ısı artışı görülür ve tedavide %98 fayda görülür. Zamanında yapılan sempatektomi ile ellerde uzuv kaybı yaşanmaz.



