Non-surgical varicose vein treatment is a method of treatment with modern techniques that allows enlarged and dysfunctional veins to be closed without the need for surgical intervention. Venablock and foam therapy are the two most preferred and effective techniques among these methods. The goal of both methods is to disable varicose veins and redirect blood circulation to healthy veins.
Venablock treatment is a method in which varicose veins are closed by injecting a special adhesive into the vein. During this procedure, local anesthesia is applied and a thin catheter is inserted through the vein. The adhesive bonds the inner surfaces of the vein together, stopping the blood flow, and the varicose vein is eventually absorbed by the body and disappears. One of the biggest advantages of Venablock is that it does not require the use of bandages or compression stockings after the procedure and the patient can immediately return to their daily life. In addition, complications such as pain, infection and scarring are extremely rare with non-surgical varicose vein treatment because it is minimally invasive.
Foam therapy is a technique in which a medicated foam is injected into the varicose vein, disabling it. The foam adheres to the inner surface of the vessel, causing it to narrow and close. This method can be used effectively for more superficial and medium-sized varicose veins. Foam therapy can be easily performed in an office setting and usually requires only a few sessions. The medication used during the procedure acts only on the varicose area within the vein and does not damage other healthy veins in the circulation.
Both methods are much more comfortable than surgical procedures and the recovery period after the procedure is extremely short. Venablock is generally effective for larger and deeper varicose veins, while foam therapy is preferred for superficial varicose veins that cause aesthetic concerns. In both methods, the patient can stand up immediately after the procedure and resume daily activities.
| Treatment Method | Description |
| Foam/Fluid Sclerotherapy (UGFS) | The vein is closed by injecting a sclerosing substance into the varicose vein. It is especially effective for small/medium vessels. |
| Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) | The vessel is closed by applying laser energy into the vessel. Success rate is high, recovery time is short. |
| Radio Frequency Ablation (RFA) | The vessel is closed from the inside by applying radio frequency energy to the vessel wall. It causes less pain and bruising. |
| Medical Adhesive (VenaSeal) | The vein is plugged with biological adhesive. No heat or anesthesia is required. Compression stocking is not needed most of the time. |
| High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) | The vessel is destroyed with sound waves through the skin. It is a completely non-invasive method. |
| Cryo-Laser Sclerotherapy (CLaCS) | It is a combination of cold air, laser and foam injection. Suitable for aesthetic purposes for side veins. |
| Compression and Electrostimulation | Compression sore throat and devices reduce symptoms by supporting circulation. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Regular exercise, leg elevation and avoidance of prolonged standing/sitting are recommended. |

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul
>Turkey’s Cardiovascular Surgery Doctor
What is Varicose Veins and For Which Reasons ‘Non-Surgical Varicose Veins Treatment’ is Required?
The veins in our legs are a wonderful system that fights against gravity and transports blood back to the heart. Inside these veins are tiny one-way valves that prevent the blood from sliding back downwards. When the structure of these valves breaks down, the blood escapes backwards and begins to pool inside the vessel. Just as a balloon expands when too much air is pressed into it, the vessel in which the blood accumulates expands, lengthens and becomes tortuous over time. We call this condition varicose veins.
Varicose veins are not just an appearance problem. It is a medical condition that can seriously impair quality of life if left untreated. There are some important risk factors that play a role in the development of varicose veins:
Some of these risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition (family history)
- Progressive age
- Female gender (hormonal influences)
- Pregnancy
- Being overweight
- Occupations that require prolonged standing or sitting
- Sedentary lifestyle
- If you have one or more of these symptoms in your legs, it may be time to consult a specialist.
- Visible by eye, tortuous veins
- Pain and aching
- Feeling of heaviness and fullness
- Increased fatigue in the evening hours
- Itching or burning in the legs
- Night cramps
- Heat in the ankles (edema)
- In advanced cases, skin discoloration and hardening
- Non-healing wounds (venous ulcer)
These symptoms are a sign of an underlying venous insufficiency and modern non-surgical varicose vein treatment methods have been developed precisely to address these problems.
How to Take the First Step for the Right Varicose Veins Treatment?
The road to a correct varicose vein treatment necessarily passes through a correct diagnosis. The gold standard for this diagnosis is Color Doppler Ultrasonography. This examination is a completely painless and harmless method that works with sound waves, allowing us to draw a detailed road map of the vascular system in your legs. During this procedure, while you are standing, we get a clear picture of the blood flow in the veins, whether the valves are working or not, and how far back there is a valve in which vein.
Planning treatment without this vascular map is like setting off without knowing the address. Doppler shows us the source of the problem, so that treatment can be planned directly to this source. With this method, we realize that your visible varicose veins are actually caused by a defect in a main vein that starts in the groin and is invisible to the eye. We also target the treatment to that main vessel. A comprehensive Doppler examination is therefore the cornerstone of successful treatment.
Why Classical Varicose Veins Surgery is No Longer the First Choice?
Years ago, the only solution for treating varicose veins was classical surgery, in which the vein was surgically pulled out by cutting through the groin and wrist. While this method was effective, it was quite a challenge for the patients.
- These old types of surgeries had some disadvantages.
- Requirement for general anesthesia or lumbar anesthesia
- Necessity of hospitalization
- Severe postoperative pain
- Large and diffuse bruises on the legs
- Weeks-long recovery process
- Permanent stitch marks
- Risk of damage to the nerves around the vessel
Today, this picture has completely changed. Thanks to the non-surgical varicose vein treatment techniques that have been developed, instead of “ripping out” the vein, we now “close it from the inside” where it is located, through a pinhole. This is a much more comfortable approach that is at least as successful as conventional surgery, if not more so.
Why are the Reviews of Those Who Have Varicose Veins Treatment with Laser Generally Positive?
Laser varicose vein treatment (Endovenous Laser Ablation – EVLA) is one of the longest used non-surgical methods and its success and reliability have been proven by tens of thousands of scientific studies. Patients’ satisfaction after this treatment is high because of the comfort and effectiveness of the procedure.
So, how is laser varicose vein treatment performed? The main problematic vein identified by Doppler is entered with a thin needle, usually at knee level. Through this needle, a hair-thin fiber (laser wire), which produces laser light at its tip, is advanced along the vein and placed at the starting point of the thigh. All of these stages are monitored on the ultrasound screen.
Then one of the most important steps of the procedure, called “tumescent anesthesia”, is performed. This is the injection of a fluid containing cold serum and local anesthetic into the vasculature around the laser wire. This fluid not only completely numbs the area, providing zero pain, but also acts as a shield protecting the surrounding tissues (skin, muscles, nerves) from the heat of the laser. After anesthesia, laser energy is delivered and the fiber slowly retracts. This energy destroys the inner wall of the vessel in a controlled manner, causing it to shrink and close instantly. Over time, the body destroys this closed vessel on its own.
Laser treatment has major advantages:
- Performed with local anesthesia
- Approximately 30 minutes duration
- Does not require hospitalization
- Return to normal life on the same day
- No incisions and stitches
- Long-term success rate above
How is non-surgical varicose vein treatment performed with radiofrequency?
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is another popular thermal treatment method based on the same principle as laser. It uses radiofrequency waves instead of laser light as the energy source. The process steps are very similar to laser. Again, a special catheter is inserted into the vein through a needle puncture. The tip of this catheter heats up to 120°C in a controlled manner, shrinking and closing the vessel wall.
One of the most important elements of radiofrequency treatment is the thurasan anesthesia. Compared to laser, there are studies that show that post-procedure pain and bruising can be somewhat less, which can take patient comfort a step further. Both laser and radiofrequency are reliable methods with proven long-term results that are among the best varicose vein treatment options.
What is Varicose Veins Treatment with Adhesive, the Most Comfortable Method?
This method, known as medical adhesive or biological glue (VenaSeal), is a revolutionary technology that maximizes comfort in the treatment of varicose veins. This method does not use heat and is therefore a “non-thermal” technique.
In the procedure, a thin catheter is inserted into the problem vessel, again under ultrasound guidance. Through this catheter, tiny drops of “cyanoacrylate”, a special medical adhesive that is fully compatible with the tissues, are injected into the vein. After each injection, gentle pressure from the outside ensures that the vessel walls stick together and seal instantly. In short, the vessel is sealed from the inside out.
This method has some very important advantages that set it apart from others:
There is no need for tumescent anesthesia. Since no heat is used, dozens of injections are not made around the vein. Only the single point where the catheter enters is anesthetized.
There is usually no obligation to wear varicose veins stockings after the procedure. This is a great relief, especially in the summer months.
Pain and bruising are almost non-existent.
The healing process is the fastest. Patients can return to their lives immediately after the procedure without restrictions.
Due to this unique comfort, it is an ideal option, especially for patients who have a fear of needles or who do not want to use varicose veins shoes.
What are the Prices for Non-Surgical Varicose Veins Treatment?
One of the issues that patients are most curious about is naturally the cost of the treatment. Non-surgical varicose vein treatment prices are a factor that varies according to the person and the situation, rather than a fixed figure.
The main factors affecting cost are:
Technology to be used: Each method – laser, radiofrequency, adhesive (VenaSeal) – has its own device and consumable costs. In particular, the newest technology, the adhesive method, can be more costly than others.
Prevalence of the disease: Is the problem only in one leg and one main vein, or do both legs and multiple veins need treatment? The number and length of vessels to be treated directly affect the cost.
Need for Additional Treatment: In addition to the main vein treatment, the price is also determined by whether additional procedures such as foam therapy (sclerotherapy) or miniflebectomy are required for visible varicose veins.
Experience of the Clinic and the Physician: The technological equipment of the center where the treatment is performed and the experience of the physician performing the procedure in this field is also a factor.
Why are the Reviews of Those Who Have Varicose Veins Treatment by Root Positive?
Foam therapy (ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy) is a very effective method we use especially for the treatment of the remaining, close to the skin, tortuous and green-colored veins or capillaries after the main vein problem has been solved.
In this method, a special medicine called sclerosant is mixed with air to form a foam. This foam is injected directly into the varicose vein with very fine needles. By pushing the blood, the foam makes full contact with the vessel wall and initiates a reaction there, causing the vessel to shrink and eventually be destroyed by the body.
There are reasons why the reviews and satisfaction of those who have undergone varicose vein treatment with foam are high:
- It is a very fast and practical process.
- It is almost painless.
- It does not require stitches or incisions.
- The aesthetic results are quite successful.
- Ideal for very tortuous veins that laser or radiofrequency cannot reach.
- It can be applied as a complementary treatment in the same session as the main vascular treatment.
How to Treat Varicose Veins in a State Hospital?
Yes, today many non-surgical varicose vein treatments are successfully performed in the cardiovascular surgery clinics of public and university hospitals. In particular, basic thermal methods such as laser (EVLA) and radiofrequency (RFA) have become standard services in many public hospitals.
The answer to the question of how to treat varicose veins in a public hospital is similar to private centers as a process. First of all, you need to be examined by making an appointment with a cardiovascular surgery outpatient clinic. If deemed necessary, the doctor will refer you for a Doppler ultrasound. If you are found suitable for non-surgical treatment after the results have been evaluated, you will be given a day for the procedure.
But there may be some differences.
Waiting Times: Due to the high volume in public hospitals, waiting times between examination, Doppler and treatment appointments may be longer than in private centers.
Technology Options: Depending on the capabilities of the hospital, the latest technologies such as the adhesive (VenaSeal) may not always be available. Generally, laser and radiofrequency are more common.
Complementary Treatments: The scope of aesthetically-oriented complementary treatments, such as foam therapy or miniflebectomy, may vary from hospital to hospital.
What are the Truths and Fallacies about Varicose Veins Treatment at Home?
It is very important to have the right information about methods such as “varicose veins treatment at home” or “varicose veins treatment with lemon” circulating on the internet or among the public. It is important to remember that the underlying problem of varicose veins is a damaged vein valve. This is a mechanical problem and unfortunately no cream, herb or rose can repair this broken valve. Creams containing horse chestnut or some herbal pills can temporarily relieve symptoms such as pain and a feeling of heaviness by tightening the vessel wall somewhat, but this does not treat the underlying disease.
So, is there nothing you can do for your heirs at home? Of course there is. Although they do not cure the disease, they can reduce your symptoms and slow its progression.
Here are some useful habits you can practice at home:
- Do regular walking
- Swim
- Cycling
- Maintaining ideal weight
- Eating fibrous foods
- Reducing salt consumption
- Avoid staying in a standing or sitting position for long periods of time
- Resting by lifting the legs up whenever possible
- Avoiding tight clothing and high heels
- Wearing varicose veins stockings in the pressure recommended by your doctor.
After Non-Surgical Varicose Veins Treatment
| Treatment Type | Endovenous laser/radiofrequency ablation, sclerotherapy, adhesion (VenaSeal), foam treatment. |
| Recovery Cycle | Return to daily life is usually possible within 1-2 weeks; full recovery may take 2-6 weeks. |
| Physical Activity | Same-day walking is recommended; prolonged standing or inactivity should be avoided. |
| Compression stockings | It is generally recommended to use compression stockings for at least 6-8 hours a day for 1-2 weeks after the procedure. |
| Drug Use | Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed if necessary; short-term anticoagulant therapy in some patients. |
| Wound and Entry Site Care | The access site should be kept clean and dry and signs of infection should be monitored. |
| Complications | Subcutaneous stiffness, discoloration, transient pain, rarely deep vein thrombosis, pigmentation may be present. |
| Leg Position | Keeping the legs elevated while sitting is recommended; it reduces edema and promotes venous return. |
| Nutrition | A low-salt, balanced diet to reduce edema is recommended; no special restrictions are usually required. |
| Smoking and Alcohol | Not recommended; adversely affects vascular health, may delay recovery. |
| Sexual Activity | Depending on the general situation, it can be started within 2-3 days; if there is pain or tenderness, it can wait. |
| Psychological Support | High satisfaction in terms of aesthetics and quality of life can be achieved; support is offered in case of concern. |
| Vehicle Handling | It is usually possible to use the tool on the day of the procedure or the next day. |
| Controls | The vascular closure status is checked by Doppler ultrasound in the first 7-10 days after the procedure and then at intervals of 1-3 months. |
Blog Yazıları
Heart Disease: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » Heart Disease: Types, Causes, and SymptomsHeart diseases are [...]
Aug
How the Heart Works
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » How the Heart WorksThe heart functions as a [...]
Aug
How Many Hours Does Heart Valve Surgery Take?
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » How Many Hours Does Heart Valve Surgery Take?Heart [...]
Aug
How long does coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery take?
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » Coronary Artery Bypass » How long does coronary artery bypass [...]
Aug
Kalp Kapak Değişimi Ameliyatı Nedir? Kalp Kapak Değişimi Nasıl Yapılır?
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » Kalp Kapak Hastalıkları » Kalp Kapak Değişimi Ameliyatı Nedir? Kalp [...]
Aug
Kalp Kapakçığı Tamiri ve Kalp Kapakçığı Değişimi Arasındaki Fark
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » Kalp Kapakçığı Tamiri ve Kalp Kapakçığı Değişimi Arasındaki [...]
Aug
Life After Heart Valve Surgery
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » Life After Heart Valve SurgeryLife after heart valve [...]
Aug
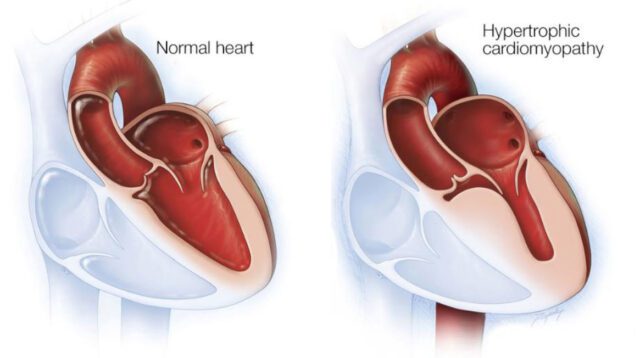
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Symptoms & Treatment
Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul » General » Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Symptoms & TreatmentHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a [...]
Aug