It is a structure located between the right ventricle of the heart and the pulmonary artery, allowing blood to flow in one direction towards the lungs. Like other heart valves, it prevents blood from flowing backwards. However, some individuals may have congenital or later developing problems with this valve. In such cases, pulmonary valve surgery It allows blood to flow in one direction to the lungs. However, sometimes if this valve does not work properly, it can prevent healthy blood circulation.
İçindekiler Tablosu
Why is Pulmonary Valve Surgery Important?
Pulmonary valve surgery Why is it important? It's a structure located between the right ventricle of the heart and the pulmonary artery, and it allows blood to flow in one direction to the lungs. A healthy valve ensures that blood moves smoothly from the heart to the lungs.
It occurs when the valve leaflets stick together or become abnormally thick. When the valve narrows, it becomes harder for the right ventricle to pump blood to the lungs. This can cause the heart to work too hard and eventually weaken the heart muscle. When the valve leaflets don't close properly, blood leaks backwards into the right ventricle. In the long term, this backflow can cause the right ventricle of the heart to enlarge and malfunction.
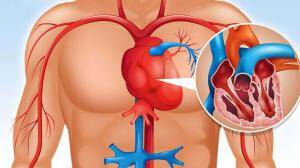
Congenital Valve Defects, sometimes individuals are born with an abnormal structure. Such congenital defects may be caused by the valve structure being missing or abnormal. Endocarditis is an inflammatory condition caused by infection on it. Endocarditis can cause damage to the valve structure, which leads to deterioration of valve function.
Disorders that occur in the pulmonary valve make it difficult for it to pump oxygenated blood. This can cause individuals to experience shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain and other symptoms. These symptoms can lead to serious discomfort in daily life and a decrease in quality of life. Pulmonary valve surgery The goal is to restore valve function and prevent symptoms from developing. Surgery may be done to repair, widen, or completely replace the valve structure. This depends on the patient's condition, the severity of the valve defect, and other health conditions.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Valve Disease
Symptoms of pulmonary valve disease vary depending on the severity, duration, and underlying cause. However, if any of these symptoms are experienced, a cardiologist should be consulted. Early diagnosis, pulmonary valve surgery and can improve the patient's quality of life.
People with the disease often experience shortness of breath, especially during physical activity. In some severe cases, this shortness of breath can be felt even at rest. Patients can tire quickly as a result of decreased oxygen levels in the blood. Valve disorders can cause chest pain or discomfort. Pulmonary valve disease can cause irregular heart rhythms.
Blue or purple changes may be observed in the lips, nails or skin. This may indicate low oxygen levels in the blood. Swelling may occur in the feet and legs due to the heart not being able to pump enough blood. Feeling faint or fainting episodes may occur during or immediately after physical activity. Some patients may also develop a persistent or chronic cough.
Stages of Pulmonary Valve Disease
Diagnostic tests are determined based on the physical examination and the patient's symptoms. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can slow the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications. If you are experiencing symptoms related to the pulmonary valve, you should consult a cardiologist.
In the mild stage, signs and symptoms are usually very mild or absent. There is usually no limitation in routine physical activities. There is mild valve stenosis or insufficiency. Diagnostic tests such as echocardiograms may detect mild abnormalities. No specific treatment is usually needed, but regular checkups are important.
In the middle stage, they may notice symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or rapid heartbeat. Valve stenosis or insufficiency is more obvious. Moderate valve abnormalities may be detected on an echocardiogram. Treatment with medications or minimally invasive procedures may be necessary.

In the severe stage, symptoms can be felt even at rest. Symptoms such as shortness of breath, severe fatigue, chest pain, and fainting are common. The risk of complications in the heart and lungs increases. There is severe valve stenosis or insufficiency. Significant abnormalities are observed on echocardiograms and other diagnostic tests. More aggressive treatment methods, such as surgery, are usually recommended.
In the final stage, the pumping capacity of the heart is severely reduced. Symptoms of heart failure appear. Fluid accumulation in the lungs and severe edema may develop. Symptoms are severe even at rest. Response to medical treatment is reduced. Surgical intervention and emergency pulmonary valve surgery should.