İçindekiler Tablosu
Carotid Artery Disease, Symptoms and Treatment Methods
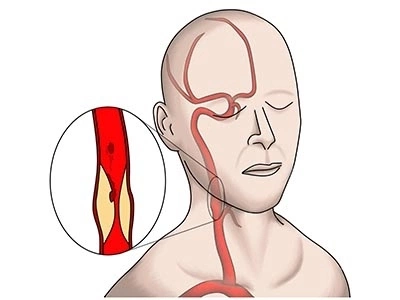 Carotid Artery Carotid arteries, popularly known as the jugular vein, are located on both sides of our neck. Carotid artery disease is an extremely serious disease as it can cause stroke, paralysis and death. In cases of stenosis, clot formation and blockage in the carotid arteries, insufficient blood flow to the brain may occur. In addition, blockages in the brain vessels may occur as a result of the fatty plaques formed in the carotid arteries breaking off and advancing into the brain vessels. Therefore, having a healthy structure of the carotid artery is extremely important for our vital functions.
Carotid Artery Carotid arteries, popularly known as the jugular vein, are located on both sides of our neck. Carotid artery disease is an extremely serious disease as it can cause stroke, paralysis and death. In cases of stenosis, clot formation and blockage in the carotid arteries, insufficient blood flow to the brain may occur. In addition, blockages in the brain vessels may occur as a result of the fatty plaques formed in the carotid arteries breaking off and advancing into the brain vessels. Therefore, having a healthy structure of the carotid artery is extremely important for our vital functions.
Article Content
-
Complaints of Carotid Artery Patients
-
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Disease
-
Causes of Carotid Artery Disease
-
Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms
-
Carotid Artery Disease Treatment Methods
-
Carotid Artery Surgery
1. Complaints of Carotid Artery Patients
In some cases, carotid artery disease can progress without any symptoms. In some patients, stroke may be the first symptom of the disease. In addition, fainting, loss of sensation and movement, headache, facial paralysis and some speech disorders may be signs of the disease. The degree of narrowing or occlusion in the carotid artery is the determinant of the conditions that occur. In cases of sudden blockage, a process that causes paralysis or death may occur.
2.Carotid Artery Diagnosis of your disease
Definitive diagnosis of carotid artery disease is made by clinical examination, carotid ultrasonography and, if necessary, carotid angiography.
3. Causes of Carotid Artery Disease
The most important reason for the emergence of carotid artery disease is the deterioration of the vascular structure and insufficient blood flow as a result of narrowing or occlusion in the carotid vessels. In some cases, complete blockage may occur. Factors that lead to the deterioration of this vascular structure and carotid artery disease include genetic factors, as well as smoking, high levels of fat and cholesterol in the blood, atherosclerosis, that is, narrowing of the vessels as a result of arteriosclerosis, diabetes, high blood pressure, a sedentary life, and excess weight. At this point, it is especially beneficial for people with cardiovascular disease to have their carotid vessels checked.
4. Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms
Carotid artery diseases can occur without symptoms. However, the main symptoms resulting from narrowing or occlusion in the carotid arteries are as follows:
- intense headache
- Temporary or permanent vision loss
- Loss of sensation and movement
- fainting, dizziness
- Facial paralysis
- Some speech and comprehension disorders
5. Carotid Artery Disease Treatment Methods
The vessels that flow from the heart to the brain, passing through the neck and irrigating the brain, are called carotid arteries. In short, it is the jugular vein. Occasional blockages may occur in the jugular veins, just like in the coronary arteries. In particular, genetic factors as well as factors such as obesity, diabetes and high cholesterol accelerate this. In case of sudden blockage, blood flow to the brain will decrease due to the clot formed on it, which may cause a stroke. For this reason, it is beneficial for patients, especially those with neurological complaints, to consult their physician from time to time.
In the treatment of carotid artery disease, with early diagnosis and evaluation of diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure, which are among the risk factors that can cause the disease, drug treatment can be applied to prevent vascular occlusions. In addition, the risk of complications is tried to be reduced and support is provided with an active lifestyle that prioritizes vascular health, includes a healthy and balanced diet, and includes exercise. Treatments for carotid artery disease include interventional methods and surgical interventions. The surgery, called carotid endarterectomy, is performed to ensure adequate blood flow by removing clots or plaques that cause blockage in the carotid artery. Additionally, among the interventional methods, there are applications in which the carotid artery is widened and a stent is inserted, which is preferred for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
6. Carotid Artery Surgery
It is referred to as carotid endarterectomy. in carotid artery surgery; Plaque in the carotid arteries is removed and the vessel is widened. After the surgery, patients should act according to the recommendations of the specialist physician, use blood thinners and anticoagulants regularly, and avoid factors that harm vascular health.
Make an Appointment