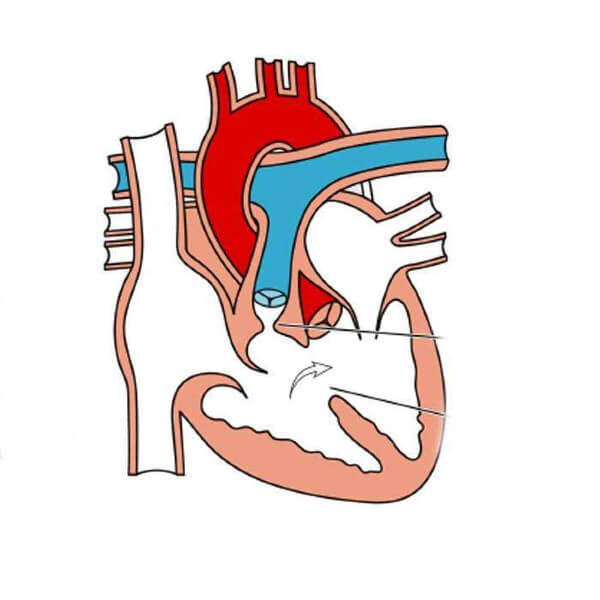
Eisenmenger sendromu, doğuştan kalp delikleri (örneğin ventriküler septal defekt, atriyoventriküler septal defekt veya patent duktus arteriozus) nedeniyle akciğer damarlarına uzun süre yüksek basınçlı kan gitmesi sonucu gelişen, geri dönüşsüz pulmoner hipertansiyon tablosudur.
Başlangıçta sol-sağ şant şeklinde olan kan akışı, akciğer damarlarındaki basıncın artmasıyla tersine dönerek sağ-sol şanta dönüşür. Bu durumda oksijeni azalmış kan, sistemik dolaşıma karışır ve vücutta morarma (siyanoz) görülür.
Belirtiler arasında nefes darlığı, çabuk yorulma, dudak ve tırnaklarda morarma, parmaklarda çomaklaşma, baş dönmesi ve bayılma yer alır. Zamanla kalp yetmezliği ve ritim bozuklukları gelişebilir.
Tedavi, semptom kontrolü ve yaşam kalitesinin korunmasına yöneliktir. Pulmoner damar genişletici ilaçlar, oksijen tedavisi ve ritim düzenleyici tedaviler uygulanabilir. Kesin tedavi seçeneği olarak kalp-akciğer nakli düşünülebilir, ancak en önemlisi erken dönemde doğuştan kalp defektlerinin tedavi edilmesidir.
| Tanım | Doğuştan kalpte büyük delik (VSD, ASD, PDA gibi) nedeniyle başlangıçta soldan-sağa olan şantın, zamanla akciğer damarlarında basınç artışına ve akciğer hipertansiyonuna yol açıp sağdan-sola şanta dönüşmesiyle ortaya çıkan sendrom |
| Nedenler | Büyük ventriküler septal defekt (VSD), atriyal septal defekt (ASD), patent duktus arteriozus (PDA) gibi doğumsal kalp hastalıkları; tedavisiz bırakılan uzun süreli şantlar |
| Risk Faktörleri | Doğuştan kalp hastalığı varlığı, erken tanı ve tedavi edilmemiş büyük kalp delikleri, ailesel yatkınlık |
| Belirtiler | Morarma (siyanoz), nefes darlığı, çabuk yorulma, parmak uçlarında çomaklaşma, bayılma, egzersiz intoleransı, hemoptizi (kanlı balgam), çarpıntı |
| Tanı Yöntemleri | Fizik muayene, ekokardiyografi, EKG, akciğer grafisi, kardiyak kateterizasyon, oksijen saturasyonu ölçümü |
| Tedavi Yöntemleri | Destek tedavisi (oksijen, diüretik, kan sulandırıcı), pulmoner vazodilatör ilaçlar, egzersiz kısıtlaması, ileri olgularda kalp-akciğer nakli |
| Komplikasyonlar | Kalp yetmezliği, aritmi, kan pıhtılaşması, beyin ve diğer organlara emboli, ani ölüm |
| Önleme Yöntemleri | Doğumsal kalp hastalıklarının erken tanı ve zamanında tedavisi, düzenli kardiyolojik takip |
Eisenmenger Sendromu Nedir?
Eisenmenger sendromu, doğuştan kalpte bulunan büyük bir delik (örneğin ventriküler septal defekt) nedeniyle uzun süre kirli ve temiz kanın karışması sonucu akciğer damarlarında geri dönüşü olmayan basınç artışı (pulmoner hipertansiyon) gelişmesiyle ortaya çıkan ciddi bir durumdur. Bu sendromda başlangıçta kalpten akciğere doğru olan kan akışı zamanla tersine döner ve vücuda oksijenden fakir kan pompalanır. Hastalarda morarma, çabuk yorulma, nefes darlığı ve bayılma görülebilir. Tedavisi zordur; ileri vakalarda akciğer ve kalp-akciğer nakli gerekebilir.
Eisenmenger Sendromu Vücutta Nasıl Bir Değişime Yol Açar?
Eisenmenger sendromunun gelişimini anlamak için kalbi ve akciğerleri karmaşık bir su tesisatı sistemi gibi düşünebiliriz. Normalde bu sistemin sol tarafı, temiz ve oksijenli suyu (kanı) yüksek basınçla tüm eve (vücuda) pompalar. Sağ taraf ise daha düşük basınçla, kirlenmiş suyu (oksijeni azalmış kanı) arıtma tesisine (akciğerlere) gönderir.
Doğuştan gelen bir kalp kusuru, örneğin iki pompa odacığı arasında bir delik (şant) olduğunda, bu sistemde bir sızıntı başlar. Tazyikli su her zaman daha az tazyikli olan yere doğru akacağından, sol taraftaki yüksek basınçlı temiz kanın bir kısmı bu delikten sağ tarafa kaçar ve temizlenmiş olmasına rağmen tekrar akciğerlere yollanır. Bu akciğerlerin hem kapasitesinin çok üzerinde bir kan akışıyla “su baskınına” uğramasına hem de normalden daha yüksek bir basınca maruz kalmasına neden olur.
Akciğerlerdeki ince ve narin damarlar, böylesine bir su baskını ve basınca dayanacak şekilde tasarlanmamıştır. Yıllar boyunca bu strese maruz kaldıklarında, kendilerini korumak için bir tepki verirler: duvarları kalınlaşır, sertleşir ve iç boşlukları giderek daralır. Tıpkı paslanan ve içi kireçle dolan su boruları gibi, bu damarların içinden kan geçirmek giderek zorlaşır. Bu durum akciğerlerdeki kan basıncının tehlikeli seviyelere çıkmasına, yani pulmoner arteriyel hipertansiyona (PAH) yol açar.
Süreç ilerledikçe, akciğerlerdeki direnç o kadar artar ki kalbin sağ tarafındaki basınç, sol taraftaki basıncı geçer. İşte bu “Eisenmenger noktası” denilen kritik eşiktir. Artık sızıntının yönü tersine döner. Kalbin sağ tarafındaki oksijeni azalmış “kirli” kan, temizlenmek için akciğerlere gidemez; bunun yerine kalpteki delikten geçerek sol tarafa karışır ve oradan da doğrudan bütün vücuda pompalanır. Bu andan itibaren vücut, ihtiyacı olan oksijeni yeterince alamaz hale gelir. Eisenmenger sendromu bu geri döndürülemez fizyolojik değişimin adıdır.
Hangi Doğuştan Kalp Hastalıkları Eisenmenger Sendromu İçin Risk Oluşturur?
Eisenmenger sendromu, sistemik ve pulmoner dolaşım arasında büyük bir geçişe izin veren ve zamanında müdahale edilmemiş herhangi bir kalp anomalisinden kaynaklanabilir. Ancak her doğuştan kalp kusuru aynı riski taşımaz. Riskin büyüklüğü ve sendromun ortaya çıkma hızı, kusurun yerine ve büyüklüğüne bağlıdır.
Bu sendroma yol açabilen başlıca kalp kusurları şunlardır:
- Ventriküler Septal Defekt (VSD)
- Atriyal Septal Defekt (ASD)
- Patent Duktus Arteriyozus (PDA)
- Atriyoventriküler Kanal Defekti
- Trunkus Arteriyozus gibi daha karmaşık ve nadir kusurlar
Ventriküler Septal Defekt (VSD), kalbin ana pompalama odacıkları olan karıncıklar arasında bir delik olmasıdır ve en sık görülen nedendir. Bu delik, sol karıncığın yüksek basıncını doğrudan akciğer dolaşımına maruz bıraktığı için, akciğer damarlarındaki hasar genellikle hızlı ve agresif bir şekilde gelişir. Bu nedenle VSD’ye bağlı Eisenmenger sendromu genellikle yaşamın daha erken dönemlerinde, hatta çocukluk çağında ortaya çıkma eğilimindedir.
Atriyal Septal Defekt (ASD) ise kalbin üst toplama odacıkları olan kulakçıklar arasında bir deliktir. Burada durum biraz daha farklıdır. Sorun ani bir basınç yüklenmesinden ziyade, yıllar boyunca akciğerlere giden kan miktarının (hacminin) sürekli olarak fazla olmasıdır. Bu kronik hacim yüklenmesi, damarlarda daha yavaş bir hasara yol açar. Sonuç olarak ASD kaynaklı Eisenmenger sendromu çok daha nadirdir ve tipik olarak çok daha ileri yaşlarda, genellikle 40’lı yaşlardan sonra yetişkinlikte kendini gösterir.
Patent Duktus Arteriyozus (PDA), vücudun ana atardamarı olan aort ile akciğer atardamarı arasındaki bir bağlantının doğumdan sonra kapanmaması durumudur. Bu açık kalan damar, aorttaki yüksek basınçlı kanın sürekli olarak akciğerlere sızmasına neden olur. Etkisi VSD’ye benzer şekilde hızlıdır ve sendromun genellikle bebeklik veya erken çocukluk döneminde gelişmesine yol açabilir.
Ayrıca Down sendromu (Trizomi 21) gibi genetik durumlar da önemli bir risk faktörüdür. Down sendromlu bireylerde doğuştan kalp kusurları daha sık görülmekle kalmaz, aynı zamanda bazı kanıtlar bu kişilerin akciğer damar hastalığını daha hızlı geliştirme eğiliminde olabileceğini de göstermektedir.
Eisenmenger Sendromu Hangi Belirtilerle Kendini Gösterir?
Eisenmenger sendromunun belirtileri, vücudun oksijen açlığı çekmesi ve kalbin yüksek akciğer basıncına karşı umutsuzca mücadele etmesinin bir yansımasıdır. Bu belirtiler genellikle yavaş yavaş ortaya çıkar ve zamanla kötüleşir. En sık karşılaşılan ve dikkat edilmesi gereken belirtiler bulunur.
Sendromun temel belirti ve bulguları şunlardır:
- Siyanoz (özellikle dudaklarda, tırnak yataklarında mavimsi-mor renk)
- Çomak parmak (parmak uçlarının genişleyip yuvarlaklaşması)
- Başlangıçta eforla gelen, sonra dinlenirken de olan nefes darlığı
- Günlük aktiviteleri bile engelleyen kronik yorgunluk ve bitkinlik
- Göğüs üzerinde baskı hissi veya ağrı
- Düzensiz, hızlı veya güçlü hissedilen kalp atışları (çarpıntı)
- Özellikle ayağa kalkarken veya efor sırasında baş dönmesi ve bayılma
- Akciğerlerdeki hassas damarların çatlamasıyla oluşan kanlı öksürük
- Sağ kalp yetmezliğine bağlı olarak bacaklarda, ayak bileklerinde ve karında şişlik
Eisenmenger Sendromu Tanısı İçin Hangi Yöntemler Kullanılır?
Eisenmenger sendromunun teşhisi, tek bir teste değil bir dizi bulgunun bir araya getirilmesine dayanan dikkatli bir dedektiflik sürecidir. Bu süreç hastanın şikayetlerini dinlemekle başlar ve kesin kanıtları ortaya koyan daha karmaşık testlere doğru ilerler. Amaç sadece sendromun varlığını saptamak değil aynı zamanda altta yatan kalp kusurunu belirlemek ve akciğerlerdeki hasarın derecesini ve geri döndürülemez olup olmadığını netleştirmektir.
Tanı sürecinde başvurulan temel testler ve incelemeler şunlardır:
- Detaylı tıbbi öykü ve fizik muayene
- Elektrokardiyogram (EKG)
- Ekokardiyogram (EKO)
- Kan testleri (Tam Kan Sayımı ve diğerleri)
- Göğüs röntgeni
- Sağ Kalp Kateterizasyonu
Bu testlerden Ekokardiyogram (EKO), yani kalbin ultrasonu, tanının temel taşlarından biridir. EKO sayesinde doktor, kalbin yapısını detaylı olarak görebilir, altta yatan VSD veya ASD gibi kusurları tespit edebilir, kalbin sağ tarafındaki büyüme ve kalınlaşmayı ölçebilir. En önemlisi, Doppler tekniği ile akciğer atardamarındaki basıncı tahmin ederek pulmoner hipertansiyonun varlığına dair güçlü kanıtlar elde eder ve kan akışının yönünü görerek sağdan sola şantı doğrulayabilir.
Ancak tanıyı kesinleştiren ve hastalığın ciddiyetini netleştiren “altın standart” test, Sağ Kalp Kateterizasyonudur. Bu işlem anjiyografiye benzer şekilde kasık veya kol damarından girilerek kalbe ve akciğer atardamarına ulaştırılan ince bir kateter yardımıyla yapılır. Bu sayede tahminlere dayanmak yerine, doğrudan kalbin içindeki ve akciğerlerdeki basınçlar ölçülür. Bu ölçümler, pulmoner hipertansiyonun şiddetini ve akciğer damarlarındaki direncin geri döndürülemez seviyelere ulaşıp ulaşmadığını matematiksel olarak ortaya koyar. Bu test, bir hastanın Eisenmenger sendromu olup olmadığının ve ameliyat şansını tamamen yitirip yitirmediğinin nihai teyididir.
Eisenmenger Sendromu İçin Hangi Tedavi ve Yönetim Stratejileri Uygulanır?
Eisenmenger sendromu tanısı konulduğunda, hastalığın seyrini tersine çevirecek bir “tedavi” maalesef mevcut değildir. Akciğer damarlarındaki hasar kalıcıdır ve bu aşamada kalpteki deliği kapatmaya yönelik bir ameliyat, durumu düzeltmek yerine ölümcül olabilir. Çünkü o delik, artık aşırı yüksek basınç altındaki sağ kalp için bir nevi “emniyet supabı” görevi görmektedir. Onu kapatmak, sağ kalbin aniden iflas etmesine neden olur.
Bu nedenle yönetim stratejisi tamamen değişir. Amaç hastalığı yok etmek değil onunla yaşamayı öğrenmek, semptomları hafifletmek, komplikasyonları önlemek ve hastanın yaşam kalitesini olabildiğince artırmaktır. Bu ilaç tedavileri ve dikkatli bir yaşam tarzı yönetimini içeren kapsamlı bir yaklaşım gerektirir.
Modern ilaç tedavileri, doğrudan sorunun kaynağı olan daralmış akciğer atardamarlarını hedef alır. Bu “hastalık hedefli tedavilerin” amacı, bu damarları gevşetmek ve genişletmektir. Böylece akciğerlerdeki basınç düşürülür, kalbin iş yükü hafifletilir ve vücuda daha fazla oksijen gitmesi sağlanır. Bu amaçla kullanılan üç ana ilaç grubu vardır. Bu ilaçlar tek başına veya birlikte kullanılarak hastaların nefes darlığını azaltır, egzersiz kapasitesini artırır ve genel olarak daha iyi hissetmelerini sağlar.
İlaç tedavisinin yanı sıra günlük yaşamda dikkat edilmesi gereken bazı kritik noktalar bulunur:
- Yeterli ve düzenli sıvı tüketimi (susuz kalmamak)
- Deniz seviyesinden 1500 metreden daha yüksek rakımlı yerlerden kaçınmak
- Vücut ısısını aniden artıran ve kan basıncını düşüren sauna, kaplıca, çok sıcak banyo gibi ortamlardan uzak durmak
- Uzman onayı ve gözetimiyle yapılan, rekabetçi olmayan hafif egzersizler (örneğin yürüyüş)
- Grip ve zatürre (pnömokok) aşılarının düzenli olarak yapılması
- Endokardit riskini azaltmak için titiz diş ve ağız bakımı
- Hem anne hem de bebek için hayati risk taşıdığından gebelikten kesin olarak kaçınmak ve bunun için güvenilir doğum kontrolü yöntemleri kullanmak
Son çare olarak medikal tedavilerin yetersiz kaldığı ve hastanın durumunun hızla kötüleştiği çok ileri evre vakalarda kalp-akciğer nakli düşünülebilir. Ancak bu taşıdığı yüksek riskler ve uygun donör organ bulmanın zorluğu nedeniyle sadece çok dikkatli seçilmiş az sayıda hasta için geçerli bir seçenektir.
Eisenmenger Sendromu Vücutta Başka Hangi Sorunlara Neden Olabilir?
Eisenmenger sendromu, etkileri sadece kalp ve akciğerlerle sınırlı kalmayan, zamanla tüm vücudu etkileyen sistemik bir hastalıktır. Kronik oksijen eksikliği ve organların bu duruma uyum sağlama çabası, bir dizi ciddi komplikasyona zemin hazırlar.
Kanla ilgili ortaya çıkabilecek sorunlar şunlardır:
- Vücudun oksijen eksikliğini telafi etmek için aşırı miktarda kırmızı kan hücresi üretmesi (sekonder eritrositoz)
- Aşırı hücre üretimiyle kanın yoğunlaşması ve akışkanlığının azalması (hiperviskozite)
- Hem damar içi pıhtı (tromboz) hem de kanama eğiliminin aynı anda artması gibi paradoksal bir durum
Kalple ilgili gelişebilecek komplikasyonlar şunlardır:
- Yüksek basınca karşı sürekli çalışan sağ kalbin zamanla yorulup iflas etmesi (sağ kalp yetmezliği)
- Kalp odacıklarındaki genişleme ve strese bağlı olarak gelişen tehlikeli ritim bozuklukları (aritmiler)
- Kalp kapakçıklarının veya iç zarının iltihaplanması (infektif endokardit)
Beyin ve sinir sistemiyle ilgili riskler şunlardır:
- Vücudun başka bir yerinde oluşan pıhtının kalpteki delikten geçerek beyin damarını tıkaması (paradoksal emboli sonucu inme)
- Kanın yoğunlaşmasına bağlı olarak beyin damarlarında tıkanıklık
- Beyin apsesi riskinde artış
Diğer organlarda görülebilecek sorunlar şunlardır:
- Kronik oksijen azlığına bağlı olarak böbrek fonksiyonlarında bozulma (böbrek yetmezliği)
- Aşırı kırmızı kan hücresi yıkımına bağlı olarak ürik asit seviyelerinin yükselmesi ve gut hastalığı
- Yine artan hücre yıkımına bağlı olarak safra kesesi taşı oluşumu riskinde artış
Eisenmenger Sendromu Hastaları İçin Gelecek Beklentisi Nedir?
Eisenmenger sendromu, şüphesiz yaşam süresini etkileyen ciddi ve ilerleyici bir durumdur. Ancak bu konuda geçmişteki verilerle bugünü kıyaslamak doğru değildir. Yakın zamana kadar, bu sendroma sahip hastaların çoğu genç yetişkinlik dönemini geçemiyordu. Fakat özellikle son yirmi yılda, doğrudan pulmoner hipertansiyonu hedef alan modern ilaçların geliştirilmesi ve hastaların bu alanda uzmanlaşmış merkezlerde takip edilmesi, tabloyu önemli ölçüde değiştirmiştir.
Bugün, Eisenmenger sendromlu birçok hasta, eskiye kıyasla çok daha uzun ve kaliteli bir yaşam sürebilmektedir. Orta yaşlara, yani 40’lı, 50’li yaşlara ve hatta daha ötesine ulaşmak artık nadir bir durum değildir. Elbette prognoz hala temkinli olmayı gerektirir ve hastalığın seyri kişiden kişiye değişir. Ancak modern tıp, bu karmaşık sendromun yönetiminde büyük bir yol kat etmiştir ve gelecek için umut verici gelişmeler devam etmektedir.
Eisenmenger Sendromu Gelişimi Engellenebilir mi?
Bu sorunun cevabı net ve kesindir: Evet. Eisenmenger sendromu, modern tıbbın olanakları sayesinde neredeyse tamamen önlenebilir bir durumdur. Bu sendromun kendisi bir kader değil zamanında atılmamış adımların bir sonucudur. Önlemenin yolu, sendroma neden olan altta yatan doğuştan kalp kusurunun, akciğerlerde geri döndürülemez hasar meydana gelmeden önce, erken dönemde teşhis edilmesi ve tedavi edilmesinden geçer.
Günümüzde pediatrik kardiyoloji ve kalp cerrahisindeki gelişmeler sayesinde, VSD, ASD, PDA gibi önemli kalp delikleri ve diğer karmaşık kusurlar, artık rutin kontrollerle bebeklik veya erken çocukluk döneminde saptanabilmektedir. Bu erken teşhis sonrası yapılan başarılı cerrahi veya girişimsel (anjiyo benzeri) kapatma işlemleri, kanın akciğerlere fazladan akmasını engeller. Böylece akciğer damarları hiçbir zaman o anormal basınca ve yüke maruz kalmaz ve Eisenmenger sendromuna giden o yıkıcı süreç hiç başlamamış olur. Bu nedenle Eisenmenger sendromunun varlığı, aslında önleyici tıbbın ve erken tanının ne kadar hayati olduğunun en güçlü kanıtıdır.
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
Eisenmenger sendromu nedir?
Doğuştan kalp deliği (ASD, VSD, PDA gibi) nedeniyle oluşan uzun süreli sol-sağ şantın zamanla yön değiştirmesi sonucu gelişen, akciğer damarlarında yüksek tansiyonla karakterize ciddi bir kalp hastalığıdır.
Nasıl oluşur?
Kalpteki delikten geçen fazla kan akciğerlere gider ve akciğer damarlarında basınç artar. Zamanla bu yüksek basınç kalpteki kan akış yönünü tersine çevirir (sağdan sola şant).
Bu hastalık kalıcı mıdır?
Evet, geliştiğinde geri dönüşü olmayan kalıcı bir hastalıktır. Erken tanı ve tedavi ile önlenebilir.
Belirtileri nelerdir?
Morarma (siyanoz), nefes darlığı, çabuk yorulma, çarpıntı, baş dönmesi, bayılma ve parmak uçlarında çomaklaşma (çomak parmak) görülür.
Eisenmenger sendromu genetik midir?
Hastalığın kendisi genetik değildir ancak neden olan kalp delikleri bazı genetik sendromlarla ilişkili olabilir.
Teşhisi nasıl konur?
Ekokardiyografi, kardiyak kateterizasyon ve oksijen satürasyonu ölçümleriyle tanı konur.
Hangi kalp delikleri bu sendroma neden olabilir?
VSD (ventriküler septal defekt), ASD (atriyal septal defekt), PDA (patent duktus arteriyozus) gibi sol-sağ şant oluşturan defektler neden olur.
Bu hastalık bulaşıcı mıdır?
Hayır, Eisenmenger sendromu bulaşıcı değildir; doğuştan gelen kalp defektlerine bağlı gelişir.
Tedavisi mümkün mü?
Tam kür mümkün değildir; semptomların kontrolü ve yaşam süresinin uzatılması için medikal tedavi uygulanır.
Hangi ilaçlar kullanılır?
Pulmoner hipertansiyonu kontrol altına alan ilaçlar (bosentan, sildenafil, iloprost) ve oksijen tedavisi kullanılır.
Cerrahi tedavi yapılabilir mi?
Sendrom geliştikten sonra kalp deliği kapatılmaz. Ancak bazı uygun vakalarda kalp-akciğer nakli gerekebilir.
Hamilelikte riskli midir?
Evet, Eisenmenger sendromlu kadınlarda hamilelik yaşamı tehdit edecek kadar risklidir. Gebelikten kaçınılması önerilir.
Egzersiz yapılabilir mi?
Hafif ve kontrollü aktiviteler önerilir; yorucu egzersizlerden kaçınılmalıdır.
Bu hastalıkta yaşam süresi nasıldır?
Erken teşhis ve iyi yönetimle birçok hasta uzun yıllar yaşayabilir; ancak ciddi komplikasyon riski vardır.

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul graduated from Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine in 1989 and completed his specialization in Cardiovascular Surgery in 1996. Between 1997 and 2012, he served at Eskişehir Osmangazi University Faculty of Medicine as Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and Professor, respectively. Prof. Dr. Beşoğul, one of the pioneers of minimally invasive cardiovascular surgery in Türkiye, has specialized in closed-heart surgeries, underarm heart valve surgery, beating-heart bypass, and peripheral vascular surgery. He worked at Florence Nightingale Kızıltoprak Hospital between 2012–2014, Medicana Çamlıca Hospital between 2014–2017, and İstinye University (Medical Park) Hospital between 2017–2023. With over 100 publications and one book chapter, Prof. Dr. Beşoğul has contributed significantly to the medical literature and is known for his minimally invasive approaches that prioritize patient safety and rapid recovery.