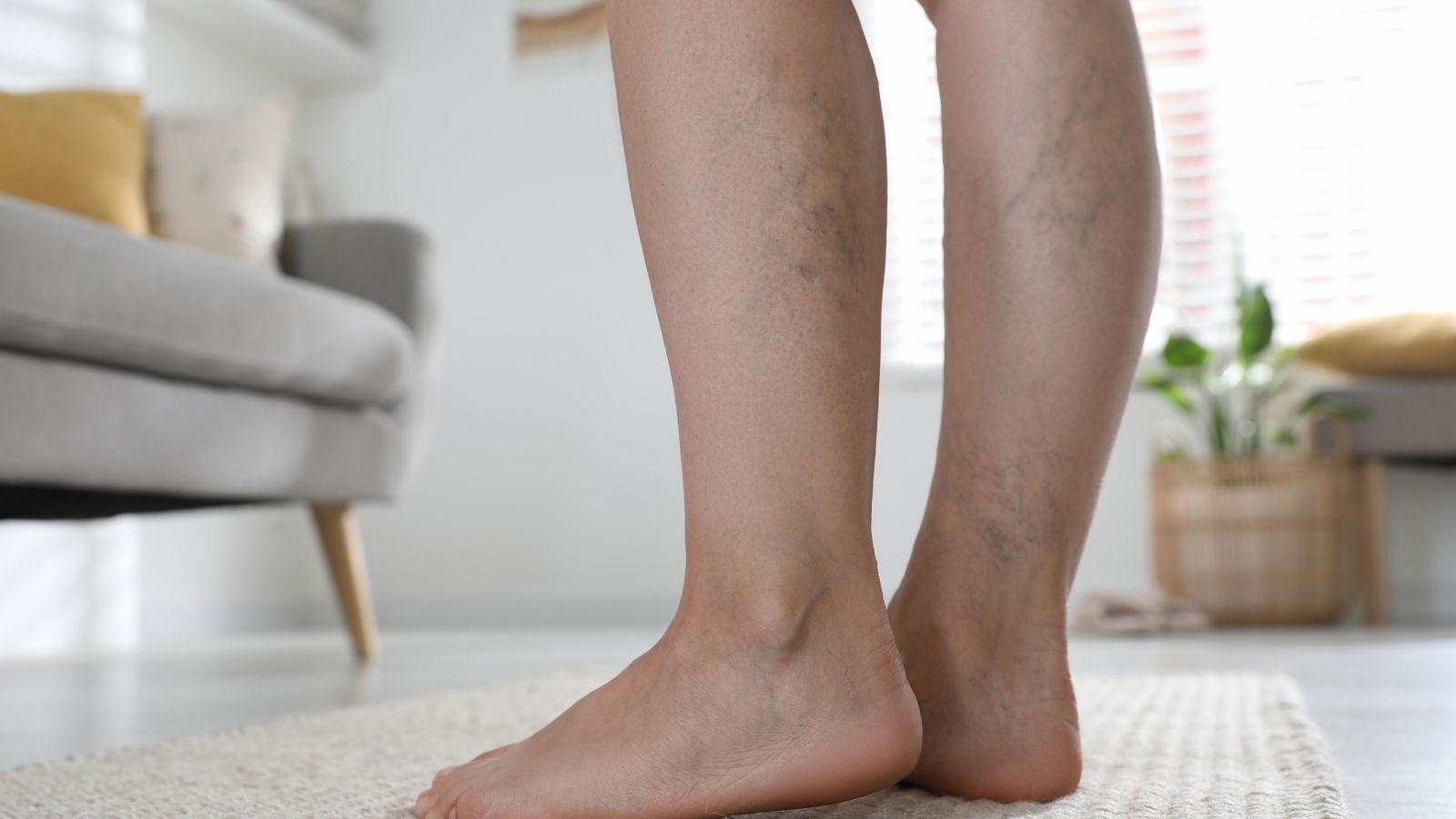
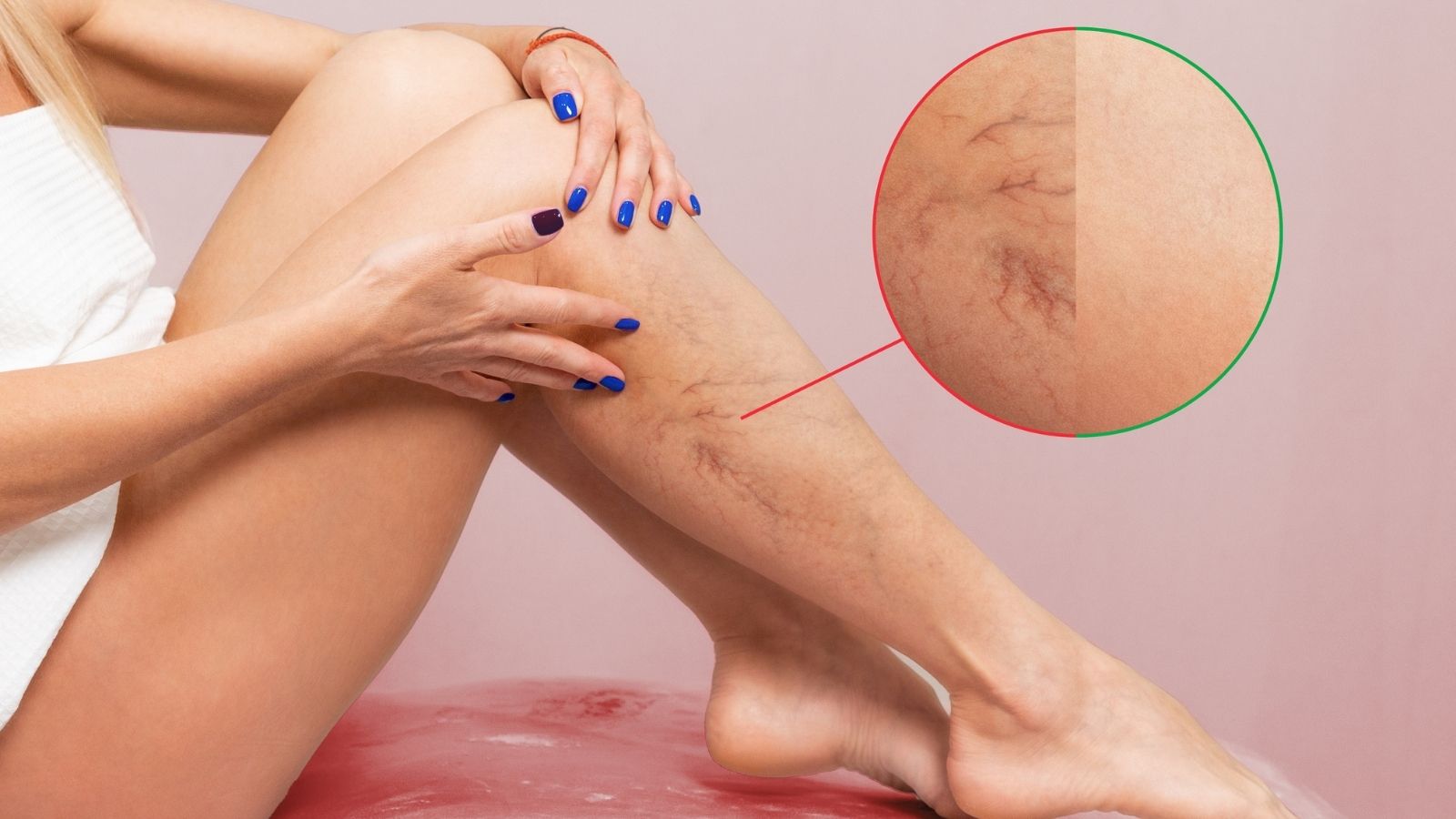
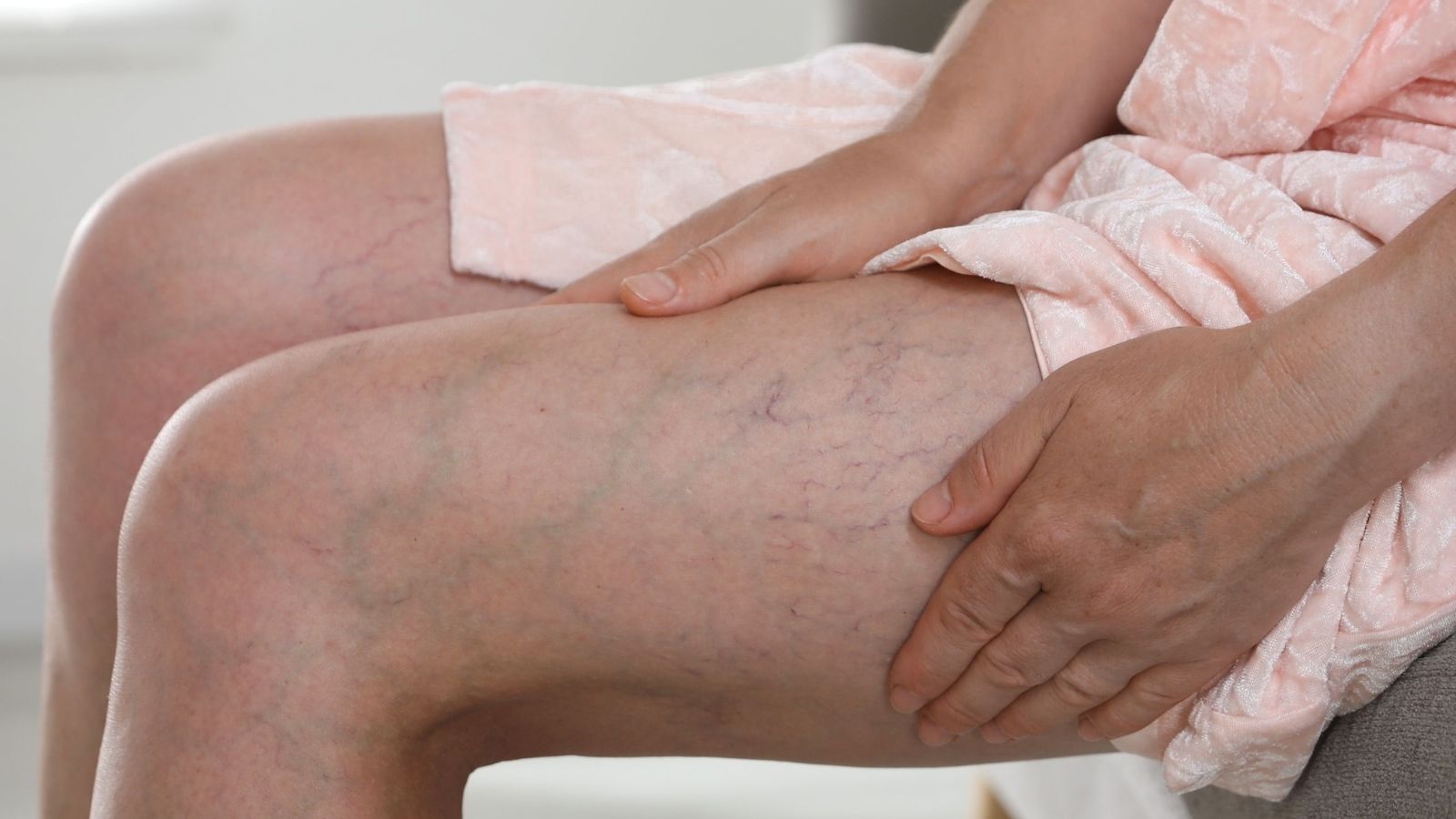
Capillary varicose vein treatment focuses on eliminating small, superficial veins that appear as red or purple lines under the skin. These veins, known as spider veins, often cause cosmetic concerns but may also indicate underlying venous insufficiency.
Sclerotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for capillary varicose veins. During this procedure, a special solution is injected into the vein, causing it to collapse and gradually disappear without damaging surrounding tissues.
Laser therapy for spider veins is another widely used method. Concentrated light beams target the abnormal vessels, sealing them off safely and improving the appearance of the skin in just a few sessions.
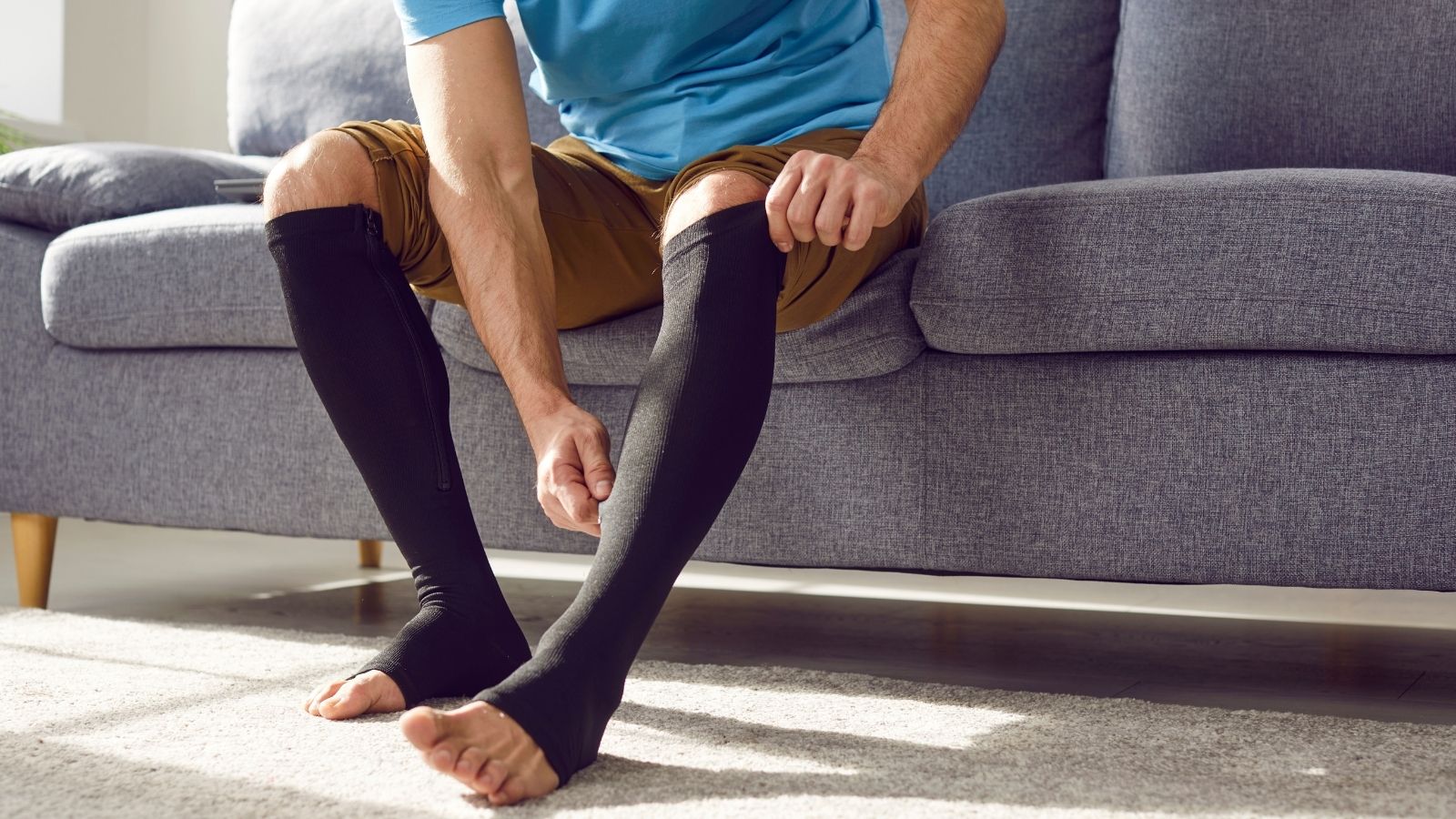
Preventive strategies for capillary varicose veins include regular exercise, avoiding prolonged standing, and using compression stockings. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of venous disorders.
| Medical Name | Telangiectasia (Capillary Varicose Veins, Spider Vein) |
| Common Symptoms | – Red, purple or blue, fine veins appearing on the surface of the skin – Usually painless – Rarely mild burning or itching |
| Causes | – Superficial vascular wall weakness- Hormone changes- Genetic predisposition- Standing for long periods of time |
| Risk Factors | – Female gender- Pregnancy- Older age- Obesity- Hormonal changes (birth control pills, menopause) |
| Complications | – Cosmetic concern – Rarely mild bleeding or skin irritation |
| Diagnostic Methods | – Physical examination – Doppler ultrasound (if necessary) |
| Treatment Methods | – Sclerotherapy- Laser therapy- Radiofrequency ablation- Lifestyle changes |
| Prevention Methods | – Avoiding prolonged standing – Regular exercise – Healthy weight control – Use of varicose veins shoes if necessary |
What is Capillary Varicose Veins and Why Should We Care?
When we talk about capillary varicose veins in everyday life, we are actually talking about two different types of vascular structures. One is “telangiectasias”, which appear just under the skin, are thin, red-purple colored, 0.5-1 mm in diameter and usually look like a network. The other is the “reticular veins”, which are slightly deeper, 1-3 mm in diameter, bluish-green in color. You can think of these reticular veins as “source veins” that supply the thin capillaries on the surface.
So why should we take these veins seriously? Because this is often only the tip of the iceberg. The main reason for the formation of these veins is that blood builds up in the veins in the legs and the pressure increases. In medical language, we call this condition “Chronic Venous Insufficiency”. In other words, those thin veins you see on the surface are actually a sign of a deeper problem, a circulatory insufficiency. Trying to just fix the appearance is like plucking only the leaves of a tree; as long as the stump remains in place, new leaves will continue to grow. So the right approach is to find the root cause of these veins and treat it. Moreover, these veins are not always silent. Many people experience some physical complaints in addition to aesthetic concerns.
Common symptoms of capillary varicose veins are as follows:
- Increased pain in the legs, especially at the end of the day
- Stinging and throbbing sensation
- Combustion
- An indescribable tingling
- Feeling of heaviness and fatigue in the legs
- Cramps, especially at night
What are the Risk Factors Leading to the Occurrence of Capillary Varicose Veins?
The veins in our legs have an amazing system that is responsible for transporting blood to the heart against gravity. The key players in this system are the one-way valves inside the veins. You can think of these valves as “swing gates” that only allow blood to flow upwards, preventing it from flowing backwards. When these gates break down, blood flows backwards and pools in the lower parts of the legs, increasing pressure. Over time, this increased pressure dilates the thin veins on the surface, forming capillary varicose veins. So what causes these valves to fail? There are some factors that initiate or accelerate this process:
The main factors that trigger the development of capillary varices:
- Genetic predisposition (family history of varicose veins)
- Being female (due to hormonal structure)
- Periods of pregnancy
- Use of birth control pills or hormone therapy
- Progressive age
- Staying in your profession for a long time (teacher, surgeon, hairdresser)
- Continuous sitting work (office workers)
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
If you have one or more of these factors, you may be more prone to capillary formation. However, this does not mean that you are helpless. Managing modifiable risk factors (weight, smoking, inactivity) plays an important role in slowing the formation of new blood vessels.
Which Doctor Should I Consult for the Treatment of Capillary Varicose Veins and How Does the Diagnostic Process Work?
Since capillary varicose veins are a vascular health problem, a specialist in Cardiovascular Surgery is a doctor who has been trained and specialized in this field. Correct treatment is only possible with an accurate diagnosis, and this diagnostic process forms the basis for effective treatment.
When you contact a specialist, the process usually works like this:
Detailed Interview and Examination: Your doctor will first listen to your complaints, how long they have been present, your lifestyle, occupation and family history of varicose veins. He will then examine your legs while you are standing to assess the extent and type of veins and whether there are other problems such as larger varicose veins, edema or skin changes.
Color Doppler Ultrasonography (RDUS): This is the sine qua non of modern varicose vein treatment. It is the most valuable tool for charting the treatment path. Thanks to this painless, harmless and radiation-free sound wave technology, the physician can visualize the vascular system under the skin in detail. But the goal is not only to see the capillaries on the surface, but mainly to identify them:
Valvular Valve (Reflux): To determine whether blood backs up in the deep veins.
Feeder Vein (Source Vein): To find the thicker source vessel, usually invisible to the eye, that feeds the surface capillary network.
Do not forget that scientific studies show that approximately ‘% of capillary varicose veins are fed from such a source vein. If this source vein is not found and treated, any intervention only on the surface capillaries will be incomplete and the veins will soon recur. For this reason, the treatment of capillary varicose veins always starts with this detailed ultrasound examination in competent clinics in major centers such as Ankara, Istanbul or Izmir. This is a critical step that maximizes the chances of success.
How to Treat Capillary Varicose Veins with Sclerotherapy (Needle Treatment)?
Sclerotherapy is a highly effective method that is recognized worldwide as the “gold standard” in the treatment of capillary and medium-sized varicose veins. It is the most commonly used method for the treatment of capillary varicose veins, especially in the legs. The logic of the process is quite simple: Using very fine needles, a special medicine called “sclerosant” is injected into the vein to be treated. This medicine irritates the inner wall of the vein, causing it to almost stick together. The body perceives this adherent vessel as a foreign substance and eventually dissolves and destroys it. Eventually the vein disappears permanently.
Sclerotherapy can be administered in two different ways depending on the form of the drug: liquid or foam.
Favorable Conditions for Foam Treatment:
- Nourishing reticular veins that are thicker
- Vascular networks spread over a large area
- Situations where a stronger impact is required
Favorable Conditions for Fluid Therapy:
- Very thin, red-colored spider veins
- Especially sensitive capillaries in the face area
- Areas where a more controlled and precise intervention is required
The foam is obtained by mixing the drug with gas and makes more effective contact with the vessel wall because it pushes the blood inside the vessel better. This makes it a more powerful option, especially in the treatment of source veins. Your physician will choose the form that is most suitable for you based on the Doppler ultrasound findings and the structure of your veins. The reviews of those who have undergone the treatment of varicose veins with a clip show high satisfaction with the effectiveness of the method, especially in more prominent veins.
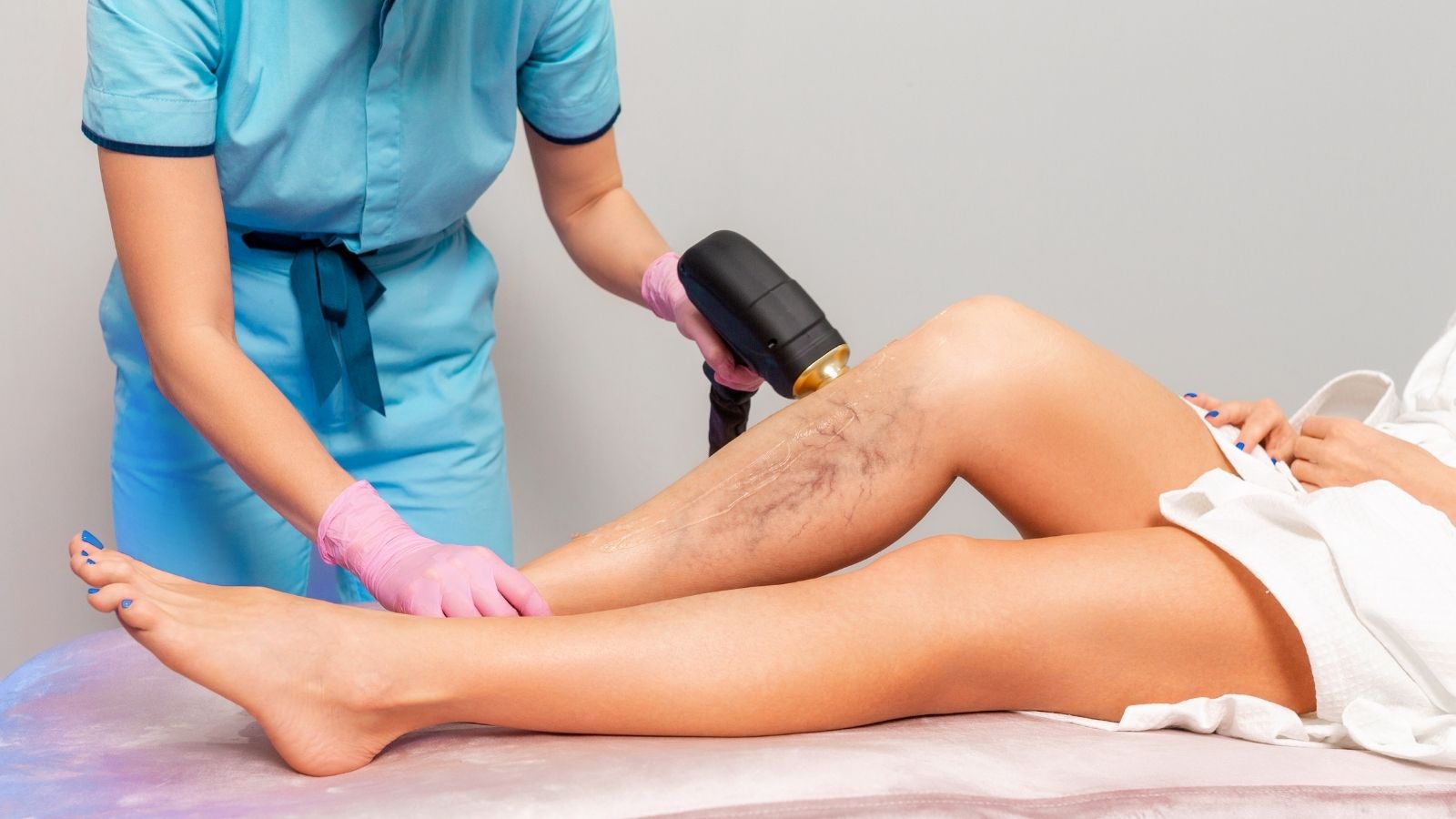
For whom is laser treatment of capillary varicose veins suitable and how does it work?
Laser treatment of capillary varicose veins is a modern treatment method that is applied through the skin and does not use needles. It is a more suitable option, especially for those looking for an alternative to sclerotherapy or for certain conditions. The principle of operation of the laser is very clever: The laser device emits a light that is only absorbed by the hemoglobin in the blood inside the vein. This light energy is converted into heat inside the vessel. This controlled heat causes the vein to shrivel and close, and over time it is destroyed by the body. Surrounding tissues are not damaged during this process. During the procedure, there is usually a slight sensation, like “a rubber band hitting the skin” and continuous cooling is applied to protect the skin.
For whom is laser treatment an ideal option?
- People with fear (phobia) of the home
- Allergic to sclerotherapy medication
- Those with red capillaries that are too thin to be penetrated with a needle
- Especially in the treatment of capillaries in the facial area
- In the removal of fine red spots called “matting” that may occur after sclerotherapy
Which Method Should Those Who Have Capillary Varicose Veins Treatment Prefer: Laser or Sclerotherapy?
This is one of the most curious issues for patients. there is no single answer to the question “What is the best varicose vein treatment for me?”. The right answer is the one that is personalized according to the structure, location and prevalence of your veins.
A Comparison for Veins in the Legs:
For the vast majority of capillaries and reticular veins in the legs, sclerotherapy is usually the first and most effective option. This is because it can treat both the surface spider veins and the source vessel that feeds them in a single session. It is also generally more cost-effective than laser. The Nd:YAG laser is a powerful alternative in cases where sclerotherapy cannot be performed on the legs (very thin veins, needle phobia).
The situation is different for facial veins:
Laser and light (IPL) treatments are arguably the most superior method for thin and red capillaries on the face. The vessels in this area are ideal for the laser to target, and the risks that sclerotherapy can pose to the delicate facial skin are absent in these methods.
What are the Recovery Process and Things to Consider After Treatment of Capillary Varicose Veins?
The success of treatment depends as much on aftercare as on the procedure. Following your doctor’s advice will both speed recovery and minimize possible side effects.
Recommendations for After Sclerotherapy:
- Regular use of varicose vein stockings for the duration prescribed by the physician
- Do plenty of walking immediately after the procedure and in the following days
- Avoiding heavy sports and strenuous activities for several days
- Avoiding hot water, sauna, Turkish bath and spa for at least 2 weeks
- Protecting treated areas from intense sunlight
Tips for After Laser Treatment:
- Applying a cold compress to the area after the procedure (soothes)
- Cleansing the skin with gentle, fragrance-free cleansers
- Strictly protect the treated area from sunlight for at least 3-4 weeks and use a high-factor sunscreen (critical to prevent staining)
- Avoiding hot environments and strenuous exercise for several days
What are the Possible Side Effects and Complications of Treatment?
As with any medical intervention, some side effects may occur in the treatment of capillary varicose veins. But the vast majority of these are temporary and easily managed.
Common and Transient Side Effects:
- Slight bruising at the site of the operation
- Redness
- Temporary tenderness or scratching
More Rare Cosmetic Side Effects:
Hyperpigmentation: Brown staining along the line of the treated vein. It is usually seen after sclerotherapy and is caused by the blood remaining in the vein shining. More than one percent of these spots disappear completely on their own within 6-12 months. Using a compression stocking reduces this risk.
Matting: The appearance of new, very fine red veins in the treated area. It is usually an extreme response of the body to the healing process and most of the time it goes away on its own. In cases where it does not, it can be easily treated with a laser.
When performed by an experienced physician with the correct diagnosis and technique, the risk of scarring or more serious complications is extremely low.
Is it Possible to Treat Capillary Varicose Veins at Home? Do Herbal Remedies Work?
On the internet and social media, we often see various cures and creams recommended under the headings “capillary varicose veins home treatment” or “capillary varicose veins treatment herbal”. Let me clarify this issue.
What Can Be Done at Home (To Alleviate Complaints):
- Resting with legs elevated at the end of the day
- Massaging the legs with cold water or applying a cold shower
- Using creams that contain ingredients such as horse chestnut extract and promote circulation
- Regularly doing sports that work leg muscles such as walking and swimming
- Achieve weight control
What Cannot Be Done at Home (To Destroy Veins):
- Eliminating a formed and structurally compromised capillary
- Repairing a broken vessel valve
- Treating the underlying venous insufficiency problem
In short, home remedies or herbal products do not destroy existing veins. They can only support circulation and help relieve symptoms such as pain and fatigue. Modern medical treatments that target and destroy these vessels are the only way to achieve a lasting solution.
How Lasting are the Treatment Results and Do Capillary Varicose Veins Recur?
This is one of the most crucial questions. The answer is twofold: Yes, the treatment results are permanent. In other words, a vein that has been successfully treated and destroyed by sclerotherapy or laser will not return.
However, the formation of varicose veins is a chronic tendency. This means that your body can continue to produce new capillaries due to your genetic makeup or lifestyle. The long-term success of treatment and slowing the formation of new blood vessels depends on the following:
Correct Diagnosis and Treatment of the Root Cause: If the source vessels detected by Doppler ultrasound are treated correctly, the risk of a stroke is greatly reduced.
Lifestyle Changes: Taking precautions after treatment, such as weight control, regular exercise and avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity, delays the formation of new blood vessels.
We can liken it to pulling weeds in a garden. If you remove the weeds at the root, they will not grow back in the same place. But new weeds may grow in another part of the garden over time. The important thing is to take care of your garden regularly. So is the treatment of capillary varicose veins; you can eradicate the existing problem and, with regular care (lifestyle and, if necessary, small reconstruction sessions), maintain the smooth and healthy appearance of your legs for many years.

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul graduated from Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine in 1989 and completed his specialization in Cardiovascular Surgery in 1996. Between 1997 and 2012, he served at Eskişehir Osmangazi University Faculty of Medicine as Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and Professor, respectively. Prof. Dr. Beşoğul, one of the pioneers of minimally invasive cardiovascular surgery in Türkiye, has specialized in closed-heart surgeries, underarm heart valve surgery, beating-heart bypass, and peripheral vascular surgery. He worked at Florence Nightingale Kızıltoprak Hospital between 2012–2014, Medicana Çamlıca Hospital between 2014–2017, and İstinye University (Medical Park) Hospital between 2017–2023. With over 100 publications and one book chapter, Prof. Dr. Beşoğul has contributed significantly to the medical literature and is known for his minimally invasive approaches that prioritize patient safety and rapid recovery.