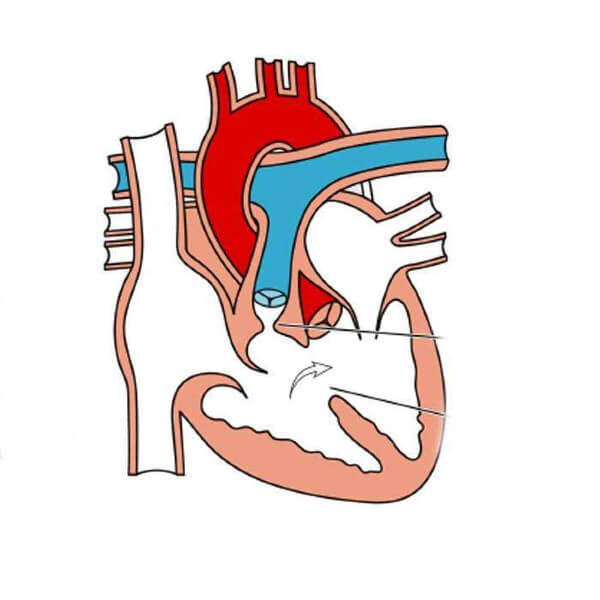
Open heart surgery success rates are high, with most patients achieving significant improvement in cardiac function. However, outcomes vary depending on age, underlying disease, and surgical complexity.
Mortality risk is generally low but increases with comorbidities such as diabetes, kidney disease, or previous heart surgery. Careful preoperative evaluation minimizes surgical risks.
Advances in surgical techniques, anesthesia, and postoperative care have improved survival rates significantly. Minimally invasive methods are being used for selected patients to reduce recovery time.
Long-term success depends on adherence to medical therapy, cardiac rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes. Regular follow-up ensures detection of complications and preservation of heart function.
What is the current success rate of open heart surgery?
Today, open heart surgeries, especially planned open heart surgeries, are much safer and more successful than feared when performed in experienced hands. These surgeries not only eliminate the immediate threat to life, but also significantly increase the life expectancy and, most importantly, the quality of life of our patients. In fact, after a timely intervention, many of our patients can have almost the same life expectancy as healthy individuals in their age group.
Coronary Bypass (CABG) and Mitral Valve Repair, the two most common operations, are the best examples of this success. While the success rate of bypass surgery performed in a good center exceeds ‘s, this rate can approach 0 in a mitral valve repair performed in suitable patients. These figures show how effectively the surgery solves the mechanical problem in the heart.
However, one must be honest here: Surgery does not treat the underlying chronic disease itself, such as atherosclerosis, but the result of it. So we are replacing a clogged pipe, but we are not completely removing the rust that causes the pipe to clog. Therefore, the lifelong benefit of the surgery depends very much on the patient’s lifestyle and regular use of medications.
Does the minimally invasive (closed) method have an impact on the risks of open heart surgery?
In heart surgery, the surgical methods we use to get to the heart are as important as the surgery itself. We basically have two different approaches: the traditional method and the minimally invasive method.
In the traditional method, the chest bone (sternum) is opened with a longitudinal incision to access the heart in the widest and most comfortable way. This is still the safest and most accurate approach, especially in patients who have problems with more than one valve, require a complex procedure on the aorta or have had previous heart surgery.
Minimally invasive surgery is popularly known as the “closed” or “axillary” method. Here, the chest bone is not cut completely. Instead, the heart is accessed through small incisions of 3-5 cm between the ribs or by opening only a small part of the lower end of the chest bone. Through these small holes, we insert special long instruments and a camera to perform the surgery. Robotic surgery is the most technological and precise version of this method.
So what are the advantages of this closed method? Studies show that the main benefit of this method is not to further reduce the already low risk of death. The real difference comes in post-operative comfort. The most obvious benefits of the minimally invasive method are the following:
- Faster recovery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced need for intensive care
- Less need for blood transfusions
- Less pain after surgery
- Lower risk of infection
- Better cosmetic result
Of course, this method is not suitable for every patient. If you ask what is the most difficult heart surgery, the answer is usually the general condition of the patient and the complexity of the procedure. Sometimes the safest way is the traditional way, which provides the best view. We make the decision by weighing all these factors on a case-by-case basis.
Is bypass surgery safer in the functioning heart (off-pump)?
Another thing you often hear about in bypass surgery is “on-pump” or “off-pump” surgery. This refers to whether or not the operation was performed using a cardiothoracic machine.
In the traditional technique (pump surgery), the patient is connected to a heart-lung machine. This machine is responsible for pumping blood into the body and oxygenating it during the operation. During this time, we stop the heart with a special inhalation. In a still and bloodless environment, it is much easier and more precise to suture millimeter vessels.
In off-pump surgery, no heart-lung machine is used. While the heart is still beating, we simply fix a small area where the vessel to be bypassed is located with a special instrument and suture it. The main purpose of this method is to avoid some of the negative effects that a heart-lung machine can have on the body (especially risks to the kidneys and brain).
So which is better? Major scientific studies show that there is no significant difference in the risk of death between the two methods. The risk of death from bypass surgery is quite low with both methods. Although off-pump surgery reduces some of the risks of complications, it can have a downside: It is technically more difficult to work on a moving heart. This may slightly reduce the long-term patency rate of the bypass vessels.
The decision is therefore entirely patient-specific. For example, for an elderly patient with a severely fractured aorta or limited renal function, the off-pump method may make more sense because it protects them from the risks of the machine. But for a patient who is large, vascularized and needs bypasses in multiple vessels, the precise operating environment provided by the on-pump method may be more critical for long-term success.
What factors increase the risk of death from heart surgery?
“Doctor, what is the risk of death from open heart surgery in this operation?” This is the most natural and justified question I have ever heard. This risk is not a standardized number; it is almost like a personalized fingerprint and depends on many factors. The conditions that most affect risk are the following:
- Advanced age (especially over 70 years)
- Low pumping power of the heart
- Presence of pre-operative renal failure
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Serious lung diseases (COPD)
- To have had a stroke before
- Performing the surgery under emergency conditions
As you can see, the risk is actually more related to the overall health of the patient than to the surgery. While the risk of a patient undergoing a planned surgery and in good general condition is extremely low, the risk of a patient with multiple organ failure who is rushed into surgery during a heart attack is naturally higher.
How many years do those who have open heart surgery live?
This is one of the most beautiful issues that allows our patients to look to the future with hope. A successful surgery is often a return to the normal flow of life.
A patient who undergoes bypass surgery can expect to live a healthier life for an average of 15-20 years if they pay attention to their postoperative lifestyle. A patient who undergoes planned surgery for aortic valve replacement or aortic aneurysm, after surviving the initial period of surgery, reaches the same level in terms of life expectancy as healthy individuals in their age group. In other words, the surgery almost turns back the clock. It is no different for a patient whose mitral valve has been successfully repaired; the expectation of a normal and quality life is extremely high.
What should be considered after open heart surgery?
The postoperative period is as important as the success of the surgery. This period is the first step towards a new and healthier life.
The most critical issue in the healing process is the fusion of the breast bone (sternum). This process takes about 3 months. During this period, there are some important rules that you must follow in order for the bone to fuse properly. Here’s what to watch out for during the first 6-8 weeks:
- Avoid driving a car
- not lifting anything heavier than 5 kilos
- Not pushing or pulling movements
- Not getting up with your arms supported from somewhere
- Avoid lying on your face or side
So when can sports be practiced after open heart surgery? It usually starts with light brisk walking after 2-3 months. However, for any kind of sporting activity, you must get your doctor’s approval and ideally participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program. These programs will teach you how to exercise safely and speed up your recovery.

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul graduated from Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine in 1989 and completed his specialization in Cardiovascular Surgery in 1996. Between 1997 and 2012, he served at Eskişehir Osmangazi University Faculty of Medicine as Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and Professor, respectively. Prof. Dr. Beşoğul, one of the pioneers of minimally invasive cardiovascular surgery in Türkiye, has specialized in closed-heart surgeries, underarm heart valve surgery, beating-heart bypass, and peripheral vascular surgery. He worked at Florence Nightingale Kızıltoprak Hospital between 2012–2014, Medicana Çamlıca Hospital between 2014–2017, and İstinye University (Medical Park) Hospital between 2017–2023. With over 100 publications and one book chapter, Prof. Dr. Beşoğul has contributed significantly to the medical literature and is known for his minimally invasive approaches that prioritize patient safety and rapid recovery.