Arrhythmia is a condition characterized by irregular heart rhythms that may be too fast, too slow, or erratic. Symptoms vary from palpitations to dizziness and can be life-threatening in severe cases.
Common types of arrhythmia include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia. Each type carries distinct risks and requires tailored management strategies.
Diagnosis relies on electrocardiography, Holter monitoring, and electrophysiological studies. Identifying the underlying cause guides appropriate treatment and risk stratification.
Treatment options range from antiarrhythmic drugs and catheter ablation to implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators. Lifestyle modification and risk factor control are also integral components of care.
| Definition | Irregular, rapid or slow beating of the heart as a result of disruption of its normal electrical activity |
| Causes | Coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, hypertension, heart failure, thyroid disorders, electrolyte imbalances, certain medications, stress, excessive caffeine or alcohol use |
| Risk Factors | Advanced age, diabetes, hypertension, obesity, history of heart disease, genetic predisposition, smoking |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, irregular heartbeat, fainting, dizziness, weakness, chest pain, shortness of breath, sometimes asymptomatic |
| Diagnostic Methods | Electrocardiography (ECG), Holter monitoring, stress test, echocardiography, electrophysiological study |
| Treatment Methods | Anti-arrhythmic drugs, beta blockers, pacemakers, cardioversion, ablation, treatment of the underlying cause |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest, decreased quality of life |
| Prevention Methods | Treatment and control of heart diseases, healthy lifestyle, regular follow-up, avoidance of harmful habits |
What is Heart Arrhythmia?
In its simplest definition, a heart arrhythmia is a malfunction in the internal electrical system that regulates the beating of your heart. Because of this disruption, the heart starts to work much faster, much slower or completely irregularly than it should.
Your heart’s main job is to pump blood throughout the body. To do this, it needs to contract in perfect timing, in a steady rhythm. When an arrhythmia occurs, this rhythm is disrupted. The heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. As a result, our brain, lungs and all our other organs don’t get the oxygen and nutrients they need. In the long term, this can lead to impaired organ functioning, permanent damage and even life-threatening conditions.
But don’t be alarmed, not every arrhythmia is dangerous. Sometimes it is so brief, such as a momentary pause or an extra beat, that it doesn’t disrupt the heart’s overall working pattern. At such moments, you either don’t feel anything or just a slight fluttering, a “purr purr”. Such conditions are generally considered harmless arrhythmias.
How is the Heart’s Normal Electrical System Affected in the Event of a Heart Arrhythmia?
To understand how a heart arrhythmia occurs, it is first necessary to know how the heart works normally. You can think of your heart as an intelligent structure with a power plant and wires running from it. The purpose of this system is to ensure that the heart chambers contract in the correct order and in harmony.
The command center of this system is a natural pacemaker in the upper right chamber of the heart, which we call the “sinus node”. This is where the first electrical signal that starts each heartbeat originates. Through special conduction pathways, this signal first causes the upper chambers of the heart (the atria) to contract. Then the signal reaches the “atrioventricular (AV) node”, a junction point. The AV node holds the signal for a very short time, measured in milliseconds. This critical waiting period allows time for the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart to fill with blood. Finally, the signal spreads to the lower chambers, causing them to contract strongly and pump blood throughout the body. In a healthy adult, at rest, this system produces a steady pulse of 60 to 100 beats per minute.
A heart arrhythmia occurs when there is a problem with this perfectly functioning electrical system. These problems can usually be grouped under three main headings:
- The sinus node, the heart’s natural pacemaker, produces too fast or too slow a signal.
- There is an interruption, slowing down or complete blockage of the normal pathways carrying the electrical signal.
- When another part of the heart takes over and starts producing abnormal and irregular electrical signals on its own.
What are the symptoms that indicate that a person has a heart rhythm disorder?
A heart arrhythmia usually presents itself with some symptoms, but sometimes it can be completely silent. These symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, depending on the type and duration of the arrhythmia. The most common symptoms of heart arrhythmia are the following:
- Palpitations in the chest
- Feeling of a bird wing flutter
- The heart beats as if it is beating against the chest cage (grunting)
- Sudden acceleration and deceleration of the heart
- Momentary pause followed by a strong beat (misfire)
- Dizziness or feeling dizzy
- Darkening of the eyes
- Shortness of breath (especially with exertion)
- Sudden and extreme fatigue of unknown cause
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Pain, pressure or a feeling of tightness in the chest
- Fainting (syncope) or feeling like fainting
- Feelings of worry and anxiety
- Cold sweating
If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms, especially chest pain, severe shortness of breath and fainting, it could be a sign of a serious problem. In such a case, it is vital to contact a health care provider immediately.
What are the Main Causes and Risk Factors for Heart Arrhythmia?
One of the most common questions our patients ask is “what causes heart arrhythmia?”. The factors that lead to arrhythmia are quite diverse and usually not due to a single cause. It is often caused by a combination of several risk factors. To make the answer to the question of why heart arrhythmia occurs more understandable, we can group the causes.
Conditions Related to the Heart Itself
Many conditions that disrupt the structure or function of the heart can also affect its electrical system and predispose to arrhythmia:
- Coronary artery disease (narrowing or blockage of the heart vessels)
- Past heart attack (infarction)
- Heart failure
- Heart valve diseases (stenosis or insufficiency)
- Diseases of the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy)
- Congenital heart diseases (congenital anomalies)
- Previous heart surgeries
Other Medical Conditions and Diseases
Sometimes the problem is not directly in the heart but in another system of the body:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Overwork of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
- Underfunctioning of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- Uncontrolled diabetes (diabetes)
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Lung diseases (such as COPD)
- Kidney diseases
- Serious infections such as COVID-19
Lifestyle and External Factors
Our daily habits and the substances we use can also directly affect the rhythm of the heart:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Excessive caffeine consumption (coffee, tea, energy drinks)
- Cigarettes and other tobacco products
- Drug abuse (especially cocaine and amphetamines)
- Some prescription or over-the-counter medicines (flu medicines, some antidepressants)
- Mineral and electrolyte imbalances in the body (potassium, magnesium deficiency, etc.)
- Severe stress, anxiety and panic attacks (also known as psychological heart arrhythmia)
- Advancing age and genetic predisposition
How is Heart Arrhythmia Classified According to Heart Rate?
To better understand heart rhythm disorders, we can basically divide them into two main groups based on heart rate: Those who beat too fast (tachycardia) and those who beat too slow (bradycardia).
- Tachycardia (Rapid Heartbeat): In this condition, the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute at rest. The heart beats so fast that it does not have enough time to fill with blood for the next beat. This causes less blood to be pumped into the body and therefore less oxygen to the organs. This can manifest itself in symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath or dizziness.
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate): In this condition, the resting heart rate drops below 60 beats per minute. When the heart rate is dangerously slow, the organs, especially the brain, do not receive enough blood. This can lead to fatigue, weakness, dizziness and even fainting. It should be noted, however, that a heart rate below 60 may be normal in athletes who exercise regularly or during sleep. A doctor’s assessment is essential to make this distinction.
What are Heart Rhythm Disorders of the Supraventricular Type?
Arrhythmias in this group are, as the name suggests, fast heart rhythms originating in the upper chambers of the heart (atria or atria). The most common types are the following:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): The most common type of permanent heart rhythm disorder we encounter. In this condition, instead of contracting regularly, the upper chambers of the heart “flutter” in a chaotic manner at very high speeds of 350-600 beats per minute. Because of this ineffective trembling, blood stagnates in the auricles and becomes prone to clotting. If a clot breaks off here and travels to the brain, a stroke can result. Therefore, atrial fibrillation is a condition that significantly increases the risk of stroke and must be treated.
- Atrial Flutter Similar to atrial fibrillation, it is also a rapid rhythm disorder. However, the electrical activity here is more regular and organized. It usually tends to turn into atrial fibrillation when left untreated.
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT): Regular episodes of very fast heartbeats that usually start suddenly and end abruptly. It usually occurs in young people without serious underlying heart disease and is not life-threatening, but the fluttering sensation is very uncomfortable.
Why Are Heart Rhythm Disorders of the Ventricular Type Considered Dangerous?
Ventricular heart arrhythmias are conditions that should be taken extremely seriously because they originate in the ventricles, the main chambers that pump blood into the body. Because these arrhythmias can suddenly stop the blood circulation, leading to sudden death, they often require emergency medical intervention.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): This is a very fast but usually regular beating of the ventricles at a rate of more than 100 beats per minute. VT episodes lasting longer than a few seconds cause the heart to fail to pump blood effectively and risk turning into ventricular fibrillation, a more deadly rhythm.
- Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib): The most urgent and deadliest rhythm disorder. It is responsible for almost all sudden cardiac deaths. In this condition, the electrical signals to the ventricles are so fast and chaotic that the heart muscle only ineffectively “vibrates” instead of contracting. The heart is unable to pump any blood, blood pressure drops suddenly and death results if not intervened by electroshock (defibrillation) within minutes.
What does premature beating heart rhythm disturbance mean?
A premature beat is an extra heartbeat within a normal heart rhythm cycle that comes earlier than it should. Patients often describe it as “my heart skipped a beat”, “it fell into a hole” or “it stopped for a moment and then beat loudly again”. This premature beat is usually followed by a short pause and then a stronger beat as the heart tries to get back into rhythm. This is usually categorized as a harmless arrhythmia and most of the time does not pose a danger. They can be triggered by stress, fatigue, caffeine or alcohol consumption. But when they occur very often (tens of thousands of times a day, for example), they can fatigue and weaken the heart muscle in the long term. It is therefore important that frequent recurrent early strokes are evaluated by a doctor.
What Diagnostic Methods Are Used in the Suspicion of a Heart Arrhythmia?
When you come to us with a suspected heart arrhythmia, we will carry out a series of investigations to confirm the diagnosis and find the underlying cause. This process begins with a detailed interview with you. Then, we use some basic and advanced tests to clarify the situation.
- Physical Examination: We get initial information about the rhythm by listening to your pulse and hearing your heart beating with a stethoscope.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): It is the cornerstone of arrhythmia diagnosis. It records the electrical activity of the heart for several minutes.
- Rhythm Holter: If your symptoms are not constant, this portable device records your heart rhythm for 24 hours, 48 hours or sometimes longer.
- Echocardiogram (ECHO): This is an ultrasound of the heart. It allows us to assess the structure of the heart, the condition of the valves and the force of contraction.
- Exertion (Stress) Test: If your symptoms occur during exertion, we will examine your heart rhythm at that time by walking you on a treadmill.
- Blood Tests: We check the electrolytes, thyroid hormones and other values in the blood to see if there is anything that could cause an arrhythmia.
What Role Do Advanced Tests Play in Diagnosing a Heart Arrhythmia?
Sometimes, although the above tests can make the diagnosis, we need further testing to determine where in the heart the arrhythmia is originating and what the most effective treatment would be. This is where Electrophysiological Study (EPS) comes in.
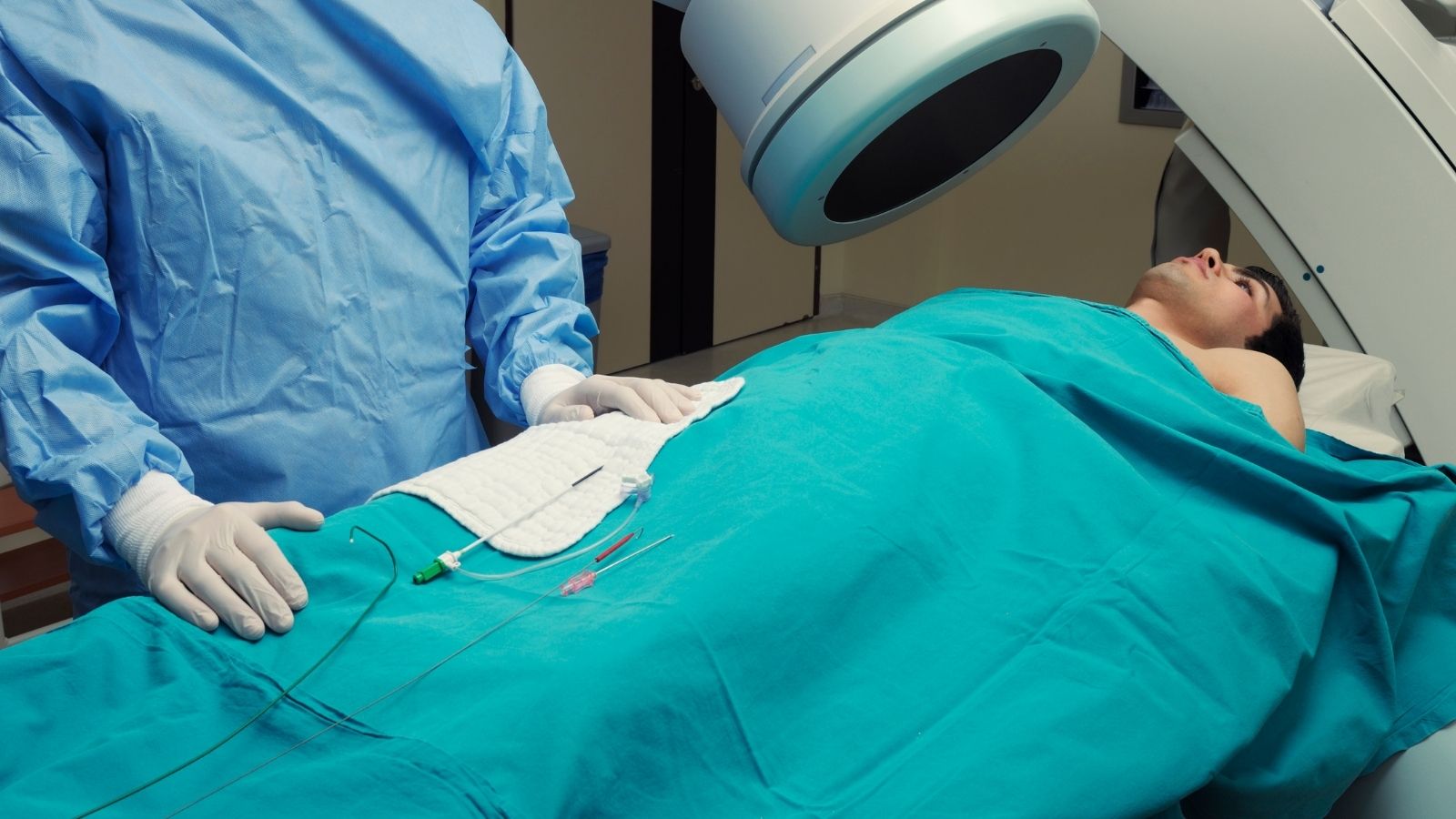
EPS is a procedure similar to angiography. Very thin, fluent catheters (wires) are inserted through a vein in the groin to the heart, which is then electrically mapped. During this process, we find the point of “short circuit” or “defective focus” that causes the arrhythmia, almost like markings on a map. This precise mapping is indispensable for the success of modern treatments, especially catheter ablation, because it shows us where we need to treat.
What are the General Approach and Goals in the Treatment of Heart Arrhythmia?
So, how is heart arrhythmia treated and what is the answer to the most curious question of our patients, “Does heart arrhythmia go away?” First of all, it should be noted that not all arrhythmias require treatment. The decision to treat is made on an individual basis, depending on the type of arrhythmia, the severity of the symptoms and the future risks. When we decide on treatment, our main goals are the following:
- To improve the patient’s quality of life by eliminating symptoms.
- To reduce the heart rate to normal limits.
- If possible, to return the heart to its normal (sinus) rhythm and keep it in that rhythm.
- Prevent blood clot formation and the associated risk of stroke in conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
- Treating the underlying heart disease causing the arrhythmia.
the answer to the question “Does a heart arrhythmia go away?” depends on the type of arrhythmia. Some arrhythmias (e.g. PSVT or atrial flutter) can be completely eliminated by catheter ablation with a success rate of over . In more complex cases, such as atrial fibrillation, the rhythm can be controlled with treatment and the vast majority of patients can return to their normal lives.
What Lifestyle Changes Are Recommended for a Heart Arrhythmia?
“What is good for heart arrhythmia?” our patients often ask. The first and most important step in treatment is always lifestyle changes. No matter how successful medications or interventional treatments are, without healthy living habits, the durability of the treatment can be compromised. Here are some tips to help regulate your heart rhythm:
- Quit smoking and all tobacco products.
- Stop or minimize alcohol consumption if possible.
- Limit caffeinated drinks (coffee, tea, cola, energy drinks).
- Reduce salt intake.
- Avoid processed, packaged and ready-to-eat foods.
- Adopt a Mediterranean-type diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains and healthy proteins.
- With your doctor’s approval, exercise regularly, such as brisk walking, at least 3-4 days a week.
- Maintain your ideal weight, and if you are overweight, lose it with the help of a dietician.
- Learn ways to cope with stress (yoga, meditation, hobbies, etc.).
- Make sure you get enough and quality sleep every night.
- If you have sleep apnea, make sure you have it treated.
How to Treat a Heart Arrhythmia with Catheter Ablation?
Catheter ablation is a highly effective and modern method of treating heart arrhythmias, which we use when drug therapy is ineffective or the patient does not want to use drugs continuously. It is based on the principle of using heat (radiofrequency) or cold (cryoablation) energy to neutralize the small, problematic area of tissue in the heart that is causing the arrhythmia.
The procedure is performed in an environment similar to an angiography laboratory, with the patient relaxed with mild sedatives. The heart is accessed with thin catheters inserted through a vein in the groin. The problematic focus is mapped with the EPS (electrophysiologic study) we mentioned earlier. Then, by energizing this target area through the tip of the ablation catheter, the tissue generating the faulty electrical signals is eliminated. Thanks to this “pinpoint” treatment, only the problematic area is treated without harming the rest of the healthy tissue of the heart. After the procedure, patients are usually discharged after one day and soon return to their normal lives.
When are devices such as pacemakers and ICDs needed in the treatment of heart rhythm disorders?
In some arrhythmias, the solution is devices that support or protect the heart from the outside.
- Pacemaker: Used when the heart’s rhythm becomes dangerously slow (bradycardia) or when the heart’s natural pacemaker fails to do its job. It consists of a small generator placed under the bridge bone and wires leading to the heart. The pacemaker activates as soon as it senses a slow rhythm, allowing the heart to beat at a normal rate.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): This device is like a guardian angel implanted in the body. It constantly monitors dangerous fast rhythms that can cause sudden death, such as ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. When it detects such a rhythm, it automatically delivers an electric shock within seconds, restoring the heart to normal and saving lives. It is usually fitted to patients at high risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
For Which Types of Heart Arrhythmias Are Surgical Methods Such as the Maze Procedure Used?
The Maze procedure is an advanced surgical rhythm disturbance treatment method that we use, especially in cases of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (AFib) that has not responded to medications and repeated catheter ablations. Usually, when a patient needs another open heart surgery, such as coronary bypass or heart valve surgery, both procedures are performed at the same time.
In this operation, the surgeon uses a special energy source to create lines of scar tissue in the upper chambers of the heart (atria) in a “maze” pattern. Since this scar tissue does not conduct electricity, it prevents the chaotic signals that cause atrial fibrillation from crossing these lines. This allows the normal signal from the heart’s natural pacemaker to travel the correct path through this maze and dominate the heart. With this method, it is possible to achieve very high success rates even in the most stubborn cases of atrial fibrillation.
What are the Potential Risks of an Untreated Heart Arrhythmia?
A serious heart rhythm disorder left untreated or neglected can lead to very serious problems over time. Knowing these risks helps us understand why it is so important to take the situation seriously.
- Stroke (stroke): Occurs when a clot in the heart, especially in atrial fibrillation, is thrown into the brain.
- Heart Failure: It is the fatigue and weakening of the heart muscle, which is constantly working inefficiently.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest (Cardiac Arrest): Sudden cardiac arrest, especially in ventricular arrhythmias, resulting in death.
- Memory Problems and Cognitive Decline: This can occur in the long term due to the constant irregular blood flow to the brain.
- Serious Decline in Quality of Life: Persistent fatigue, shortness of breath and palpitations that make a person unable to carry out daily activities.
If you have any concerns about your heart health, don’t ignore the symptoms. Remember that thanks to modern medical and surgical techniques, even the most complex arrhythmias are manageable and treatable. With the right diagnosis and a tailor-made treatment, it is possible to live a healthy and quality life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia)?
A heart rhythm disorder is a condition in which the heart beats faster, slower or irregularly than normal. It is caused by disturbances in the electrical transmission system.
What are the symptoms of arrhythmia?
The most common symptoms of arrhythmia are palpitations, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, shortness of breath and weakness.
Does arrhythmia always cause symptoms?
No. Some arrhythmias are silent and are only recognized on routine examination or ECG.
Are heart rhythm disorders dangerous?
Some arrhythmias are harmless. But some can lead to serious consequences such as stroke, heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest.
What causes arrhythmia?
Congenital heart conduction disorders, heart attack, hypertension, electrolyte imbalances, stress and certain medications can cause arrhythmias.
Does stress affect heart rhythm?
Yes, intense stress and anxiety can disrupt the heart rhythm through the nervous system.
How is arrhythmia diagnosed?
It is diagnosed with methods such as ECG, holter device (24-hour heart rhythm monitoring), effort test and electrophysiological study.
What types of arrhythmias are there?
There are different types of bradycardia (slow rhythm), tachycardia (fast rhythm), atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia.
What is atrial fibrillation?
It is a common and important type of arrhythmia in which the upper chambers of the heart (atria) work irregularly. It can pose a risk of paralysis.
Can arrhythmia be treated?
Treatment options. Treatment options include drug therapy, ablation, cardioversion and pacemakers.
When is a pacemaker inserted?
In severe bradycardia, which causes the heart to beat very slowly, a pacemaker may be needed.
Are arrhythmias hereditary?
Some types of arrhythmia may be genetically inherited. Genetic evaluation should be performed, especially if there is a history of sudden fainting or death at a young age.
Is it safe to play sports with arrhythmia?
Depending on the type of arrhythmia, exercise may be harmful in some cases. A doctor’s supervision is absolutely necessary.
Does caffeine trigger arrhythmia?
Excessive caffeine intake can cause palpitations in some sensitive people, but not for everyone.

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul graduated from Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine in 1989 and completed his specialization in Cardiovascular Surgery in 1996. Between 1997 and 2012, he served at Eskişehir Osmangazi University Faculty of Medicine as Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and Professor, respectively. Prof. Dr. Beşoğul, one of the pioneers of minimally invasive cardiovascular surgery in Türkiye, has specialized in closed-heart surgeries, underarm heart valve surgery, beating-heart bypass, and peripheral vascular surgery. He worked at Florence Nightingale Kızıltoprak Hospital between 2012–2014, Medicana Çamlıca Hospital between 2014–2017, and İstinye University (Medical Park) Hospital between 2017–2023. With over 100 publications and one book chapter, Prof. Dr. Beşoğul has contributed significantly to the medical literature and is known for his minimally invasive approaches that prioritize patient safety and rapid recovery.