Kan pıhtılaşması tromboz, damar içinde kanın pıhtı haline gelerek akışı engellemesi durumudur. Arterlerde veya venlerde meydana gelebilir ve tıkandığı bölgeye kan gitmesini önleyerek ciddi sağlık sorunlarına yol açabilir. Erken tanı, hayati komplikasyonların önlenmesinde kritiktir.
Damar içinde pıhtı oluşumu mekanizması, damar duvarı hasarı, kan akımının yavaşlaması ve pıhtılaşma eğiliminin artmasıyla açıklanır. Bu süreç Virchow triadı olarak bilinir ve derin ven trombozu, pulmoner emboli gibi durumların gelişmesinde rol oynar.
Trombozun belirtileri ve risk faktörleri, pıhtının yerine ve büyüklüğüne göre değişir. Bacakta şişlik, kızarıklık, ağrı; akciğerde ise ani nefes darlığı ve göğüs ağrısı görülebilir. Obezite, uzun süre hareketsizlik ve bazı genetik faktörler riski artırır.
Trombozun tanı ve tedavi yöntemleri, doppler ultrasonografi, BT anjiyografi gibi görüntüleme teknikleri ve pıhtılaşma testleri ile belirlenir. Antikoagülan ilaçlar, trombolitik tedavi ve cerrahi girişimler, pıhtının giderilmesi ve tekrarının önlenmesinde kullanılır.
| Bilmeniz Gerekenler | Bilgi |
| Tromboz nedir? | Kanın damar içinde normalden fazla pıhtılaşarak damar tıkanıklığına yol açmasıdır. Atardamar ya da toplardamarda gelişebilir. |
| Kan pıhtılaşmasının amacı | Kanamanın durdurulmasıdır. Ancak damar içinde gereksiz pıhtı oluşumu dolaşımı engelleyebilir ve ciddi sağlık sorunlarına yol açabilir. |
| Derin ven trombozu (DVT) nedir? | Genellikle bacak derin toplardamarlarında oluşan pıhtıdır. Bacakta şişlik, ağrı, ısı artışı ve hassasiyetle kendini gösterir. |
| Pulmoner emboli nedir? | Toplardamarda oluşan pıhtının koparak akciğer damarlarını tıkaması durumudur. Hayati tehlike oluşturabilir. |
| Arteriyel tromboz nedir? | Atardamarların içinde pıhtı oluşmasıdır. Kalp krizi (koroner arter tıkanıklığı) veya inme (beyin damar tıkanıklığı) gibi durumlara neden olabilir. |
| Trombozun başlıca nedenleri | Uzun süre hareketsizlik, cerrahi operasyonlar, travma, kalp hastalıkları, kanser, genetik pıhtılaşma bozuklukları ve bazı ilaçlar (özellikle hormon tedavileri). |
| Risk faktörleri | Obezite, sigara kullanımı, ileri yaş, gebelik, doğum kontrol hapları, varis, geçirilmiş tromboz öyküsü, immobilite (hareketsizlik). |
| Belirtiler | Etkilenen bölgede ağrı, şişlik, ısı artışı, kızarıklık, morarma, nefes darlığı (pulmoner embolide), göğüs ağrısı ve ani bilinç değişikliği. |
| Tromboz tanı yöntemleri | Doppler ultrasonografi, D-dimer testi, bilgisayarlı tomografi (BT), manyetik rezonans görüntüleme (MR), kan testleri ve anjiyografi. |
| Tedavi yöntemleri | Antikoagülan (kan sulandırıcı) ilaçlar, trombolitik tedavi (pıhtı eritici), gerekirse cerrahi müdahale ve yaşam tarzı düzenlemeleri uygulanır. |
| Antikoagülan tedavi nedir? | Kanın pıhtılaşmasını önleyerek mevcut pıhtının büyümesini engeller ve yeni pıhtı oluşumunu azaltır. Uzun süreli kullanılması gerekebilir. |
| Trombolitik tedavi nedir? | Akut ve ciddi vakalarda pıhtıyı doğrudan eritmeye yönelik ilaçlarla uygulanan tedavidir. Genellikle hastane ortamında verilir. |
| Cerrahi tedavi seçeneği | Büyük pıhtıların çıkarılması amacıyla trombektomi uygulanabilir. Bazı durumlarda damar içine filtre yerleştirilerek pıhtının akciğere gitmesi engellenir. |
| Korunma yöntemleri | Uzun süre hareketsiz kalmaktan kaçınmak, sık sık bacakları hareket ettirmek, bol sıvı tüketmek, varis çorabı kullanmak, sağlıklı yaşam alışkanlıkları edinmek. |
| Ne zaman doktora başvurulmalı? | Bacakta aniden gelişen ağrı, şişlik, renk değişikliği, nefes darlığı, göğüs ağrısı ya da bilinç değişikliği durumunda acil tıbbi yardım alınmalıdır. |
Kan Pıhtılaşması (Tromboz) Nedir?
Kan pıhtılaşması (tromboz), damar içinde normal dışı pıhtı oluşumu ile kan akışının kısmen veya tamamen engellenmesi durumudur. Bu pıhtılar, genellikle bacaklardaki derin venlerde oluşur ancak akciğer, beyin veya kalp damarlarını da etkileyebilir. Tromboz ciddi komplikasyonlara yol açabileceğinden erken tanı ve tedavi hayati önem taşır. Pıhtılaşma bozuklukları, hareketsizlik, cerrahi müdahaleler ve bazı hastalıklar riski artırır.
Kan Pıhtılaşması Neden Olur?
Vücudumuzda durup dururken bir kan pıhtısının oluşması nadiren tek bir sebebe bağlıdır. Genellikle üç ana faktörün bir araya gelmesiyle ortaya çıkan bir “kusursuz fırtına” durumudur. Bu üç temel taşı anlamak, kimlerin risk altında olduğunu ve pıhtıdan nasıl korunabileceğimizi anlamamıza yardımcı olur.
Birincisi, kan akışının yavaşlamasıdır. Damarlarımızdaki kanın sürekli ve akıcı bir şekilde hareket etmesi, pıhtılaşmayı önleyen en doğal güvencemizdir. Kan bir bölgede, özellikle de bacakların derin toplardamarlarında bir gölet gibi durgunlaştığında, pıhtılaşmayı başlatan hücreler ve maddeler birikmeye başlar. Kan akışını yavaşlatan bazı yaygın durumlar şunlardır:
- Uzun süreli yatak istirahati
- Saatler süren uçak veya araba yolculukları
- Büyük ameliyatlar sonrası hareketsizlik
- Gebelik döneminde rahmin damarlara baskısı
- Aşırı kilo (Obezite)
- Felç durumu
- Alçıya alınmış bir kol veya bacak
İkinci önemli faktör, damar duvarında hasar oluşmasıdır. Damarlarımızın iç yüzeyi, teflon gibi pürüzsüz ve kaygan bir tabaka olan “endotel” ile kaplıdır. Bu tabaka, kanın takılmadan akıp gitmesini sağlar. Bu yüzeyde bir hasar oluştuğunda, vücut bunu bir yara olarak algılar ve pıhtılaşma mekanizmasını o bölgeye çağırır. Damar duvarına zarar verebilecek durumlar arasında şunlar sayılabilir:
Cerrahi müdahaleler
- Kazalar ve kemik kırıkları
- Vücuda takılan santral venöz kateterler gibi tıbbi cihazlar
- Damar sertliği (ateroskleroz) plaklarının çatlaması
- Sigara kullanımının yarattığı kimyasal hasar
Yüksek tansiyonun damar duvarında oluşturduğu yıpranma
Üçüncü ve son ana neden ise kanın pıhtılaşmaya daha yatkın bir hale gelmesidir. Bazen kanın kimyasal dengesi, normalden daha “yapışkan” ve pıhtılaşmaya eğilimli bir yapıya bürünür. Bu durum doğuştan gelebilir veya sonradan ortaya çıkabilir. Kanın pıhtılaşma eğilimini artıran faktörler şöyledir:
- Kanser hastalığı
- Bazı genetik ve kalıtsal hastalıklar (Faktör V Leiden gibi)
- Östrojen içeren doğum kontrol hapları veya hormon tedavileri
- Vücuttaki ciddi enfeksiyonlar (COVID-19 gibi) veya iltihabi durumlar
- Gebelik ve lohusalık dönemi
- Vücudun susuz kalması (dehidratasyon)
Bu üç faktörden biri veya birkaçı bir araya geldiğinde, kanın damar içinde pıhtılaşarak tehlikeli bir süreci başlatma riski önemli ölçüde artar.
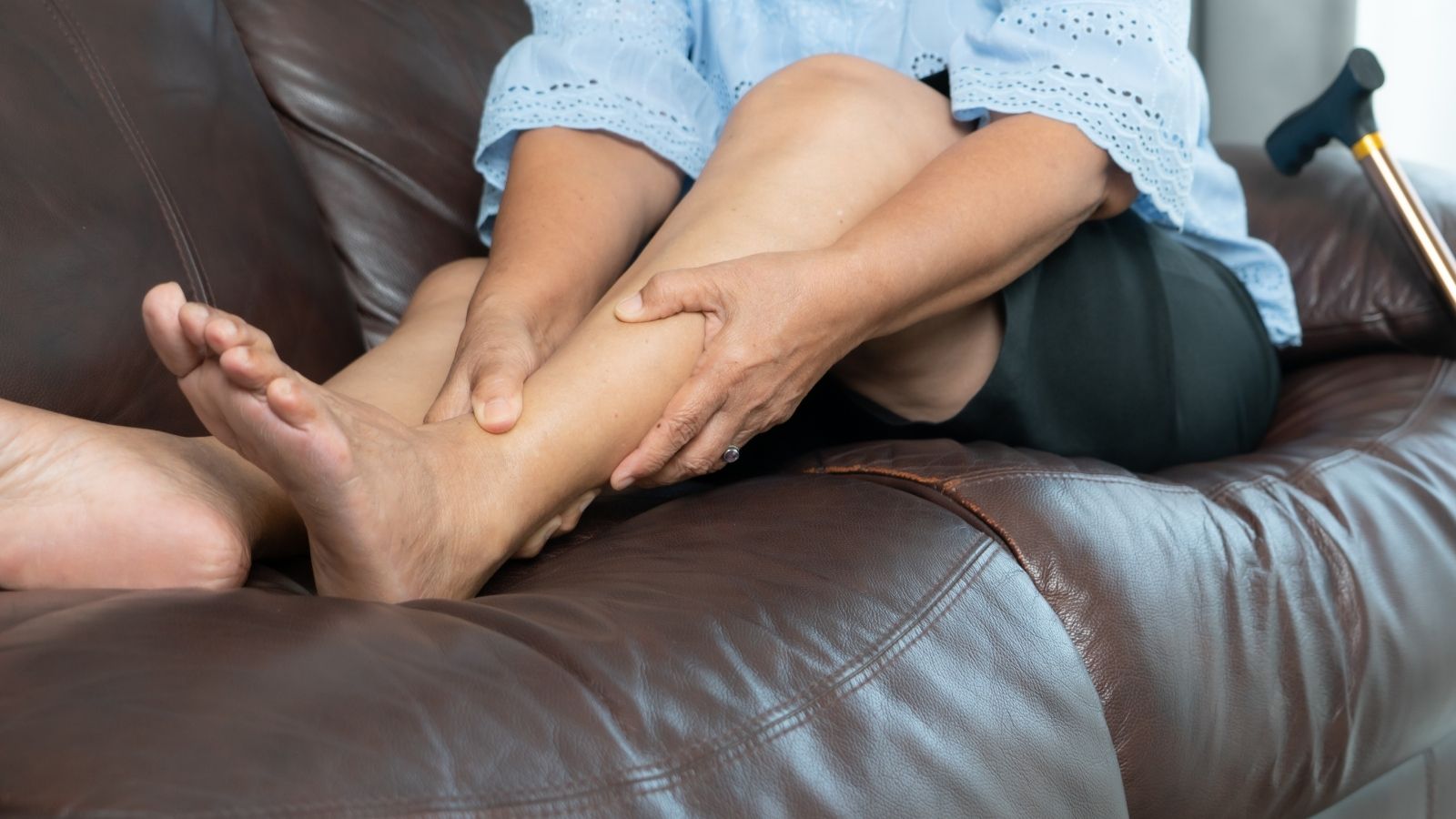
Bacakta kan pıhtısı belirtileri nelerdir?
Derin Ven Trombozu (DVT), genellikle bacakların derinlerindeki büyük toplardamarlarda bir kan pıhtısı oluşmasıdır. Bu durum kanın kalbe geri dönüş yolunu tıkadığı için bacakta bir dizi belirtiye yol açar. Ancak unutmamak gerekir ki DVT bazen çok sinsi olabilir ve hiçbir belirti vermeden de ilerleyebilir. Bu nedenle risk altındaki kişilerin daha dikkatli olması gerekir.
Bacakta pıhtı durumunda en sık karşılaşılan belirtiler genellikle tek bir bacakta ortaya çıkar ve aşağıdaki gibidir:
- Tek taraflı bacak şişliği (diğer bacağa göre belirgin fark)
- Baldırda veya uylukta hissedilen, genellikle kramp benzeri ağrı
- Yürürken veya ayakta dururken artan ağrı
- Etkilenen bölgede cildin normalden daha sıcak olması
- Ciltte kızarıklık veya morarma benzeri renk değişikliği
- Bacağa dokunulduğunda belirgin hassasiyet
Bu belirtiler pıhtının büyüklüğüne ve bulunduğu yere göre değişiklik gösterebilir. Bazen sadece hafif bir rahatsızlık hissi verirken, bazen de bacağı hareket ettirmeyi zorlaştıracak kadar şiddetli olabilir. Bu işaretlerden bir veya birkaçını fark ederseniz, özellikle de yakın zamanda bir ameliyat geçirdiyseniz, uzun bir yolculuk yaptıysanız veya başka bir risk faktörünüz varsa, durumu ciddiye alıp vakit kaybetmeden bir hekime başvurmanız hayati önem taşır. Erken teşhis, hem tedavinin başarısını artırır hem de pıhtının akciğere atması gibi ölümcül olabilecek komplikasyonları önler.
Akciğere pıhtı atması (Pulmoner Emboli) ne anlama gelir?
Pulmoner emboli, genellikle bacak damarlarında oluşan bir pıhtının (DVT) yerinden koparak kan dolaşımına katılması ve akciğerleri besleyen atardamarlardan birini tıkaması durumudur. Bu Derin Ven Trombozu’nun en korkulan ve en tehlikeli sonucudur. Akciğer damarları tıkandığında, vücudun oksijen alması engellenir ve aynı zamanda kanı akciğerlere pompalamaya çalışan kalbin sağ tarafına ani ve aşırı bir yük biner. Bu durum acil tıbbi müdahale gerektiren, hayatı tehdit eden bir tablodur.
Akciğere pıhtı atmasının belirtileri, pıhtının ne kadar büyük olduğuna ve akciğerde ne kadar geniş bir alanı tıkadığına bağlı olarak değişir. Bazen küçük bir pıhtı hafif semptomlara neden olurken, büyük bir pıhtı saniyeler içinde durumu ciddileştirebilir. En dikkat çekici ve yaygın belirtiler şunlardır:
- Aniden başlayan ve açıklanamayan nefes darlığı
- Derin nefes alırken veya öksürürken batan, keskin bir göğüs ağrısı
- Hızlı ve düzensiz kalp atışları (çarpıntı)
- Genellikle kuru olan ancak bazen kanlı balgamın da eşlik edebildiği öksürük
- Baş dönmesi, sersemlik hissi veya bayılma
Bayılma (senkop), genellikle büyük bir pıhtının ana akciğer damarlarını tıkadığının ve kalbin artık vücuda yeterli kanı pompalayamadığının bir işaretidir. Bu durumun ne kadar kritik olduğunun bir göstergesidir. Eğer bir kişide bacakta şişlik ve ağrı gibi DVT belirtileriyle birlikte yukarıda sayılan solunum şikayetlerinden herhangi biri aniden ortaya çıkarsa, bu durum bir “kırmızı alarm” olarak kabul edilmeli ve bir saniye bile beklemeden 112 Acil Servis aranmalıdır.
Atardamardaki bir kan pıhtısı nasıl sorun yaratır?
Pıhtılar sadece kirli kanı taşıyan toplardamarları değil kalbi, beyni ve diğer organları besleyen temiz kan dolu atardamarları da tıkayabilir. Atardamar tıkanıklıkları genellikle daha farklı bir mekanizmayla, damar sertliği (ateroskleroz) zemininde gelişir ve sonuçları çok daha ani ve yıkıcı olabilir.
Kalp krizi, kalbi besleyen ve koroner arter adı verilen atardamarlardan birinin kan pıhtısıyla aniden tıkanmasıdır. Bu durum o damarın beslediği kalp kası bölgesinin oksijensiz kalarak hasar görmesine ve ölmesine neden olur. Süreç genellikle damar duvarında biriken ve “plak” adı verilen yağ ve kireç birikintilerinin aniden yırtılmasıyla başlar. Vücut bu yırtığı bir kanama olarak algılar ve pıhtılaşma sistemini devreye sokarak hızla bir pıhtı oluşturur. Bu pıhtı, zaten daralmış olan damarı tamamen tıkar. Kalp krizinin en bilinen belirtileri şunlardır:
- Göğüste baskı, sıkışma veya ağırlık hissi
- Sol kola, çeneye veya sırta yayılan ağrı
- Nefes darlığı
- Soğuk terleme
- Mide bulantısı veya baş dönmesi
İnme ise beyni besleyen bir atardamarın pıhtı ile tıkanması sonucu, beynin o bölgesindeki hücrelerin oksijensiz kalarak ölmesidir. Bu durum ya beyin damarındaki bir plağın üzerinde pıhtı oluşmasıyla (trombotik inme) ya da kalpten veya boyun damarından kopan bir pıhtının beyne giderek oradaki daha küçük bir damarı tıkamasıyla (embolik inme) meydana gelir. İnme belirtileri aniden başlar ve beynin etkilenen bölgesine göre değişir. En önemli belirtileri şunlardır:
- Yüzün bir tarafında kayma veya sarkma
- Kollardan birinde ani güçsüzlük veya his kaybı
- Konuşmada bozulma, peltekleşme veya kelimeleri bulamama
- Vücudun bir yarısında uyuşma
- Ani görme kaybı veya çift görme
- Şiddetli ve ani baş ağrısı.
Kan pıhtısı şüphesinde tanı nasıl konulur?
Doğru ve hızlı bir tanı, pıhtı tedavisinin en önemli adımıdır. Tanı süreci, hastanın öyküsünü dinlemekten başlayıp, kan testleri ve gelişmiş görüntüleme yöntemlerine kadar uzanan bir dizi adımdan oluşur.
Süreç hastanın şikayetlerini ve tıbbi geçmişini (yakın zamanda geçirilmiş bir ameliyat, uzun yolculuk, kanser öyküsü vb.) dinlemekle başlar. Yapılan fizik muayene ile (örneğin bacakta şişlik, kızarıklık) pıhtı olasılığı değerlendirilir. Bu ilk değerlendirme, hangi testlerin gerekli olduğuna karar vermede yol göstericidir.
D-dimer adı verilen bir kan testi, pıhtı şüphesinde sıkça kullanılır. Bu testin en büyük değeri, sonucun negatif çıkmasıdır. Düşük pıhtı riski olan bir kişide D-dimer normal seviyelerdeyse, pıhtı olasılığı neredeyse tamamen dışlanır ve genellikle daha ileri tetkiklere gerek kalmaz. Ancak D-dimer, pıhtı dışında enfeksiyon, gebelik, ameliyat sonrası gibi birçok durumda da yükselebildiği için pozitif çıkması tek başına tanı koydurmaz. Sadece “araştırmaya devam et” sinyali verir.
Kesin tanı için kullanılan görüntüleme yöntemleri, pıhtının nerede ve ne kadar büyük olduğunu net bir şekilde ortaya koyar. Başlıca tanı yöntemleri şunlardır:
- Bacak Doppler Ultrasonografisi: Bacaklardaki DVT şüphesi için ilk tercih edilen yöntemdir. Ses dalgaları kullanılarak damarlardaki kan akışı ve pıhtının varlığı görüntülenir.
- Bilgisayarlı Tomografi Pulmoner Anjiyografi (BTPA): Akciğer embolisi şüphesi için altın standarttır. Kontrast madde verilerek çekilen bu tomografi, akciğer atardamarlarındaki pıhtıları net bir şekilde gösterir.
- BT veya MR Venografi: Standart ultrasonun yetersiz kaldığı, kasık ve karın içindeki derin damarları görüntülemek için kullanılan daha ileri yöntemlerdir.
- Damar İçi Ultrason (IVUS): Bu tanıdan çok tedaviye yön veren, devrim niteliğinde bir teknolojidir. Özellikle pıhtıyı temizlemeye yönelik bir girişim planlandığında kullanılır. Çok ince bir kateterin ucundaki minik bir ultrason probu ile damarın içine girilir. Bu sayede damar duvarı, pıhtının yapısı ve altta yatan darlık gibi sorunlar içeriden, 360 derece ve çok detaylı bir şekilde görülür. IVUS, tedavinin başarısını en üst düzeye çıkarmak için hangi boyutta bir stent kullanılacağından, tedavinin yeterli olup olmadığını kontrol etmeye kadar birçok kritik kararda cerraha yol gösteren bir “damar içi GPS” gibidir:
Kan pıhtısı için temel tedavi kan sulandırıcılar mıdır?
Evet, kan pıhtısı tedavisinin temelini ve ilk adımını antikoagülanlar, yani halk arasında bilinen adıyla kan sulandırıcı ilaçlar oluşturur. Bu ilaçların çalışma prensibi, genellikle yanlış anlaşıldığı gibi mevcut pıhtıyı eritmek değildir. Onların asıl görevi, pıhtının daha fazla büyümesini ve yerinden kopup akciğer gibi hayati organlara gitmesini engellemektir. Aynı zamanda yeni pıhtıların oluşumunu da önlerler. Bu ilaçlar pıhtıyı “kontrol altında” tutarken, vücudun kendi doğal pıhtı eritme mekanizması zamanla mevcut pıhtıyı temizlemeye çalışır.
Günümüzde kullanılan iki ana grup ağızdan alınan kan sulandırıcı vardır. Yıllardır kullanılan geleneksel seçenek Warfarin (Coumadin®)’dir. Bu ilaç etkilidir ancak kullanımı biraz meşakkatlidir. Düzenli kan testleri (INR takibi) ile dozunun sürekli ayarlanması gerekir ve birçok yiyecek ve ilaçla etkileşime girebilir.
Son on yılda ise Yeni Nesil Oral Antikoagülanlar (DOAC’lar) tedavide bir devrim yaratmıştır. Bu ilaçların Warfarin’e göre birçok üstünlüğü bulunmaktadır. DOAC’ların başlıca avantajları şunlardır:
- Etkileri birkaç saat içinde hızla başlar.
- Genellikle standart, sabit dozlarda kullanılırlar.
- Rutin kan testi takibi gerektirmezler.
- Besinlerle ve diğer ilaçlarla etkileşimleri çok daha azdır.
- Özellikle beyin kanaması gibi ciddi kanama riskleri daha düşüktür.
Bu nedenlerle güncel tedavi kılavuzları, çoğu DVT ve PE hastasında ilk tercih olarak DOAC’ları önermektedir. Tedavi süresi ise pıhtının nedenine göre belirlenir. Geçici bir risk faktörüne (ameliyat gibi) bağlı gelişen bir pıhtı için genellikle 3 aylık bir tedavi yeterli olurken, belirgin bir nedeni olmayan pıhtılarda tekrarlama riski yüksek olduğu için tedavi ömür boyu sürebilir. İlaç seçimi ve tedavi süresi, her hasta için kişiye özel olarak hekim tarafından dikkatle planlanır.
İleri evre kan pıhtısı vakalarında hangi girişimsel tedaviler uygulanır?
Kan sulandırıcı ilaçlar tedavinin temel taşı olsa da bazı durumlarda tek başlarına yeterli gelmezler. Özellikle kasıktan başlayıp karın bölgesine kadar uzanan, bacakta ciddi ağrı ve şişliğe yol açan büyük pıhtılarda (iliofemoral DVT) veya hayatı tehdit eden büyük akciğer embolilerinde, sadece pıhtının büyümesini durdurmak yetmez. Bu durumlarda, kan akışını hızla yeniden sağlamak, organ hasarını önlemek ve en önemlisi, pıhtının damarda bırakacağı kalıcı hasarın yol açtığı ve ömür boyu sürebilen “Post-Trombotik Sendrom” (PTS) adlı kronik durumu engellemek için pıhtıyı aktif olarak damardan temizleyen girişimsel tedaviler gerekir.
Bu ileri tedaviler, özellikle genç, aktif, kanama riski düşük olan ve belirtileri yeni başlamış (<14 gün) hastalarda en iyi sonuçları verir. Temel olarak iki ana yaklaşım vardır: pıhtıyı ilaçla eritmek veya mekanik olarak temizlemek.
Pıhtı Eritici Tedaviler (Tromboliz)
Bu yöntemde pıhtıyı doğrudan çözen güçlü ilaçlar kullanılır. İki farklı şekilde uygulanabilir:
- Sistemik Tromboliz: İlacın, koldaki bir damardan tüm vücuda verildiği yöntemdir. Ciddi kanama riski nedeniyle sadece hayatı tehdit eden “masif” akciğer embolisi gibi çok acil durumlarda kullanılır.
- Kateter Yönlendirmeli Tromboliz (CDT): Minimal invaziv bir tekniktir. Anjiyografi ünitesinde, kasıktaki bir damardan girilerek pıhtının içine kadar özel bir kateter ilerletilir. Pıhtı eritici ilaç, çok daha düşük bir dozda, doğrudan pıhtının kalbine verilir. Bu sayede ilacın yan etkileri azalırken etkinliği artar.
Pıhtıyı Mekanik Olarak Temizleyen Yöntemler (Trombektomi)
Bu modern yöntemler pıhtıyı fiziksel olarak parçalamak, emmek ve damardan dışarı çıkarmak için tasarlanmış özel cihazları kullanır.
- Farmakomekanik Trombektomi (PCDT): Düşük doz pıhtı eritici ilacın verilmesini, pıhtıyı ultrason dalgaları veya yüksek basınçlı su jeti ile parçalayan ve/veya vakumlayarak emen mekanik bir cihazla birleştirir. Bu kombinasyon, tedaviyi hızlandırır ve etkinliği artırır.
- İlaçsız Pıhtı Temizleme (Perkütan Mekanik Trombektomi – PMT): Bu DVT tedavisindeki en heyecan verici ve en güvenli gelişmelerden biridir. Bu teknikte, hiç pıhtı eritici ilaç kullanılmaz. Bunun yerine, damar içine gönderilen özel tasarımlı cihazlarla pıhtı yakalanır, parçalanır ve damardan tamamen dışarı alınır. Bu yöntemin en büyük avantajı, pıhtı eritici ilaçlara bağlı kanama riskini (özellikle beyin kanaması riskini) tamamen ortadan kaldırmasıdır. Tedavi genellikle tek bir seansta tamamlanır, hastanede kalış süresi kısalır ve hastalar çok daha hızlı bir şekilde normal yaşamlarına dönebilir. Bu yöntem özellikle kanama riski yüksek hastalar için ideal bir çözümdür.
Vena Kava (IVC) Filtresi bir kan pıhtısı tedavisi midir?
Bu çok önemli bir sorudur ve cevabı nettir: Hayır, IVC filtresi bir pıhtı tedavisi değildir. IVC filtresi, karın içindeki ana toplardamar olan “inferior vena kava”ya yerleştirilen, küçük, şemsiye benzeri bir cihazdır. Görevi, bacaklardan kopup gelebilecek pıhtıları, akciğerlere ulaşmadan önce bir süzgeç gibi yakalamaktır. Dolayısıyla bir tedavi değil bir koruma yöntemidir.
Geçmişte daha yaygın kullanılmış olsa da günümüzde IVC filtrelerinin kullanımı oldukça kısıtlanmıştır. Modern tıp kılavuzlarına göre, IVC filtresi takılması için tek bir net ve kabul görmüş durum vardır:
Aktif olarak pıhtısı (DVT veya PE) olan ve aynı zamanda aktif kanama gibi nedenlerle kan sulandırıcı ilaçları kesinlikle kullanamayan hastalar.
Bu durumda filtre, hasta kan sulandırıcı kullanmaya başlayana kadar geçecek sürede onu akciğer embolisinden korumak için bir “köprü” görevi görür. Kan sulandırıcı alabilen bir hastaya rutin olarak filtre takılması, faydadan çok zarar getirebilir. Çünkü uzun vadede bırakılan filtrelerin kendileri de sorun yaratabilir. IVC filtresinin potansiyel riskleri şunlardır:
- Filtrenin pıhtı ile tıkanarak bacaklarda daha şiddetli şişliğe yol açması
- Filtrenin kırılması veya yerinden oynaması
- Damar duvarını delerek çevre organlara zarar vermesi
- Uzun vadede DVT riskini artırması
Bu nedenlerle, eğer bir filtre takılması zorunluysa, mutlaka “geçici” (çıkarılabilir) bir filtre tercih edilmelidir. Hastanın kan sulandırıcı kullanmasına engel olan durum ortadan kalkar kalkmaz, filtre en kısa zamanda çıkarılmalıdır. Unutulmamalıdır ki pıhtı tedavisinin anahtarı kan sulandırıcı ilaçlar ve gerektiğinde yapılan girişimsel pıhtı temizleme işlemleridir; filtre ise sadece çok özel ve geçici durumlar için bir güvenlik ağıdır.
Kan pıhtısı geçirdikten sonra uzun vadede ne gibi sorunlar yaşanabilir?
Akut bir pıhtı olayını başarıyla atlatmak, savaşın sadece ilk yarısını kazanmak anlamına gelir. Modern pıhtı tedavisinin asıl amacı, hastanın sadece hayatta kalmasını sağlamak değil aynı zamanda uzun vadede yaşam kalitesini korumaktır. Pıhtı, tedavi edilse bile, geçtiği damarlarda kalıcı hasarlar bırakabilir ve bu da yıllar sonra bile devam eden kronik sorunlara yol açabilir.
En sık karşılaşılan uzun vadeli sorun Post-Trombotik Sendrom (PTS)’dur. Bu durum DVT (bacakta pıhtı) geçiren hastaların yaklaşık %20 ila %50’sinde görülür. Pıhtı, damar içindeki kan akışını bozarken, aynı zamanda kanın geri kaçmasını önleyen hassas kapakçıklara da zarar verir. Vücut pıhtıyı temizlese bile, bu kapakçık hasarı ve damardaki daralma kalıcı olabilir. Bu durum bacak damarlarında sürekli bir basınç artışına (venöz hipertansiyon) yol açar. PTS’nin belirtileri genellikle günün sonuna doğru veya uzun süre ayakta kalındığında kötüleşir. En sık görülen PTS belirtileri şunlardır:
- Kronik bacak ağrısı ve ağırlık hissi
- Ayak bileği ve bacakta geçmeyen şişlik
- Ciltte renk değişikliği (kahverengi lekelenmeler)
- Ciltte sertleşme ve kalınlaşma
- Yeni varislerin oluşması
- İyileşmesi çok zor olan ağrılı bacak yaraları (venöz ülser)
PTS, kişinin yaşam kalitesini ciddi şekilde düşüren, sürekli rahatsızlık veren bir durumdur. İşte tam da bu nedenle özellikle büyük pıhtılarda, pıhtıyı sadece kan sulandırıcı ile kendi haline bırakmak yerine, girişimsel yöntemlerle aktif olarak temizlemek, damar ve kapakçık hasarını en aza indirerek PTS riskini azaltmayı hedefler.
Daha nadir görülen ancak çok daha ciddi bir uzun dönem komplikasyonu ise Kronik Tromboembolik Pulmoner Hipertansiyon (KTEPH)’dur. Bu durum akciğer embolisi (PE) geçiren hastaların küçük bir kısmında (%2-4) görülür. Vücut, akciğer damarlarındaki pıhtıları tamamen eritemez ve bu pıhtılar zamanla organize olarak damar duvarına yapışır ve orada kalıcı bir skar dokusuna dönüşür. Bu durum akciğer damarlarında sürekli bir tıkanıklık ve basınç artışına yol açar. Sonuçta kalbin sağ tarafı bu yüksek basınca karşı sürekli çalışmak zorunda kalır ve zamanla yorularak kalp yetmezliğine gider. KTEPH’nin en önemli belirtisi, eforla giderek artan nefes darlığıdır. Bu durumun en umut verici yanı ise, özel bir açık kalp ameliyatı olan “pulmoner tromboendarterektomi” (PTE) ile potansiyel olarak tamamen tedavi edilebilir olmasıdır.
Benim için en uygun kan pıhtısı tedavisine nasıl karar verilir?
Bu her hastanın aklındaki en doğal ve en önemli sorudur. Modern pıhtı tedavisinin güzelliği, artık “herkese aynı gömlek” yaklaşımının terk edilmiş olmasıdır. Tedavi, tamamen kişiye özel olarak bir terzinin kişiye özel takım elbise dikmesi gibi planlanır. En doğru tedavi planına karar verilirken birçok faktör bir arada değerlendirilir.
Yolculuk, pıhtı şüphesiyle hekime başvurduğunuzda başlar. Yapılan muayene ve tetkikler sonucunda pıhtının varlığı, yeri ve en önemlisi boyutu netleştirilir. Eğer pıhtı, diz altındaki daha küçük damarlarda veya çok büyük olmayan bir akciğer embolisi ise, tedavi genellikle yeni nesil kan sulandırıcı ilaçlarla (DOAC’lar) güvenli ve etkili bir şekilde yapılır. Bu hastaların çoğu, tedavilerini evde sürdürebilir ve kısa sürede normal hayatlarına dönebilir.
Ancak eğer pıhtı büyükse, yani kasıktan karın bölgesine uzanan geniş bir DVT veya kalbin sağ tarafını zorlamaya başlayan “submasif” bir akciğer embolisi söz konusuysa, denklem değişir. İşte bu noktada sizin bireysel durumunuz devreye girer. Hekiminiz şu soruların cevabını arayacaktır:
- Yaşınız ve aktivite düzeyiniz nedir? Genç ve aktif bir bireyde, uzun vadeli yaşam kalitesini korumak ve Post-Trombotik Sendrom’dan (PTS) kaçınmak çok daha yüksek bir önceliktir.
- Belirtileriniz ne kadar şiddetli? Ciddi ağrı ve şişlik, hızlı bir rahatlama sağlamak için girişimsel tedaviyi daha anlamlı kılar.
- Pıhtı ne kadar yeni? İlk 14 gün içinde müdahale edilen taze pıhtılar, girişimsel yöntemlerle çok daha başarılı bir şekilde temizlenir.
- Kanama riskiniz nedir? Eğer kanama riskiniz yüksekse, pıhtı eritici ilaç içermeyen, sadece mekanik olarak pıhtıyı temizleyen (ilaçsız mekanik trombektomi gibi) en güvenli yöntemler ön plana çıkar.
Bu değerlendirmeler sonucunda, eğer girişimsel tedavinin faydasının risklerinden daha ağır bastığına karar verilirse, size özel bir plan oluşturulur. Bu plan, pıhtı eritici ilaçların kateterle doğrudan pıhtıya verilmesinden (CDT), pıhtının mekanik cihazlarla parçalanıp emilmesine (PCDT) veya en modern yaklaşım olan hiç pıhtı eritici ilaç kullanmadan pıhtının tamamen damardan çıkarılmasına (PMT) kadar uzanabilir.
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
Kan pıhtılaşması (tromboz) neden oluşur?
Kan pıhtılaşması için kimler daha risk altındadır?
Kan pıhtısı en sık hangi damarlarda görülür?
Tromboz belirtileri nelerdir?
Kan pıhtısı vücutta hangi komplikasyonlara yol açar?
Tromboz nasıl önlenebilir?
Hamilelikte tromboz riski neden artar?
Tromboz tedavisinde hangi yöntemler kullanılır?
Tromboz geçiren biri ne kadar sürede iyileşir?
Kan pıhtısı tekrarlar mı?

Prof. Dr. Yavuz Beşoğul, 25 yılı aşkın deneyime sahip bir Kalp ve Damar Cerrahisi Uzmanıdır. Türkiye’de kapalı kalp ve atan kalpte bypass ameliyatlarının öncülerindendir. Bugüne kadar binlerce başarılı ameliyat gerçekleştirmiş, ulusal ve uluslararası dergilerde 100’den fazla bilimsel makale yayımlamıştır.